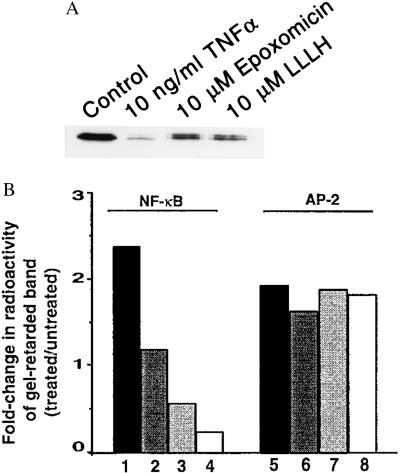
Figure 4.
Epoxomicin inhibits activation of NF-κB. (A) IκBα degradation induced by TNF-α is prevented by epoxomicin. HeLa cells were treated with epoxomicin (10 μM) or Z-LLL-H (10 μM) for 2 hr and subsequently treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 15 min. Western blot analysis of cell lysates was performed to measure IκBα levels as in Fig. 3. (B) EMSA analysis of NF-κB DNA-binding activity. HeLa cells were treated with increasing concentrations of epoxomicin for 2 hr, and, subsequently, 10 ng/ml TNF-α was added to drug-treated cells or to untreated cultures and incubated for 1 hr. Equal amounts of protein from nuclear extracts prepared from untreated and treated cultures were incubated with a radiolabeled NF-κB oligonucleotide or a control AP-2 oligonucleotide and fractionated on 4% polyacrylamide gels. Dried gels were exposed to a PhosphorImaging screen. The amount of radioactivity in the transcription factor-retarded bands was quantitated and represented as fold-change of treated over that of untreated samples. Shown are TNF-α alone (lanes 1 and 5) and TNF-α plus epoxomicin (100 nM, lanes 2 and 6; 1 μM, lanes 3 and 7; and 10 μM, lanes 4 and 8).