Abstract
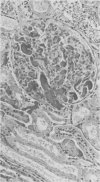
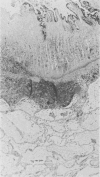
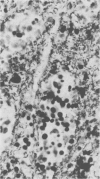
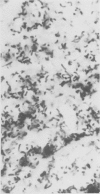
Colitis “X” is a sporadic diarrheal disease of horses with clinical signs of dehydration, electrolyte imbalances and “shock”-like features. Macroscopic and microscopic findings include signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation, necrosis of colonic mucosa and presence of large numbers of bacteria in the devitalized parts of the intestine. Recently published work suggests that the causative agent may be Clostridium perfringens, Type A, but the bacteria are recoverable only in the preliminary stages of the disease. Excess protein and lack of cellulose content in the diet is thought to be the trigger for the multiplication of the clostridial organisms. The pathological findings are pathognomonic, but clinically, a number of differential diagnoses have to be considered, such as intestinal accidents, salmonellosis, heavy metal intoxication and occlusive verminous arteritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Ekman L., Månsson I., Persson S., Rubarth S., Tufvesson G. Lethal complications following administration of oxytetracycline in the horse. Nord Vet Med. 1971 Jan;23(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows G. E., Cannon J. Endotoxemia induced by rapid intravenous injection of Escherichia coli in anesthetized ponies. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Nov;31(11):1967–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL E. J., SCHALM O. W., WHEAT J. D. ENDOTOXEMIA IN A HORSE. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1965 Jun 1;146:1300–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. Diarrhoea in the horse associated with stress and tetracycline therapy. Vet Rec. 1973 Jul 7;93(1):15–17. doi: 10.1136/vr.93.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries W. N., Strother C. W. Colitis X (exhaustion shock) in a pregnant mare. Can Vet J. 1969 Feb;10(2):48–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. M. Colitis X in the horse. N Z Vet J. 1972 Oct;20(10):190–192. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1972.34048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt A. M., Bolton J. R., Cimprich R. Differential diagnosis of diarrhoea in horses over six months of age. J S Afr Vet Assoc. 1975 Mar;46(1):73–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa R., Kern S. R. The effects of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin in Shetland ponies--clinical, morphologic and clinicopathologic changes. Vet Pathol. 1980 Nov;17(6):738–747. doi: 10.1177/030098588001700609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. Post stress diarrhoea in the horse. Vet Rec. 1975 Mar 22;96(12):267–270. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.12.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROONEY J. R., BRYANS J. T., DOLL E. R. Colitis "X" of horses. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1963 Mar 1;142:510–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney J. R., Bryans J. T., Prickett M. E., Zent W. W. Exhaustion shock in the horse. Cornell Vet. 1966 Apr;56(2):220–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer B., Searcy G. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and consumption coagulopathy. Can Vet J. 1975 Jun;16(6):151–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. T. The acute colitis syndrome. Colitis "X". Vet Clin North Am. 1973 May;3(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/s0091-0279(73)50039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]