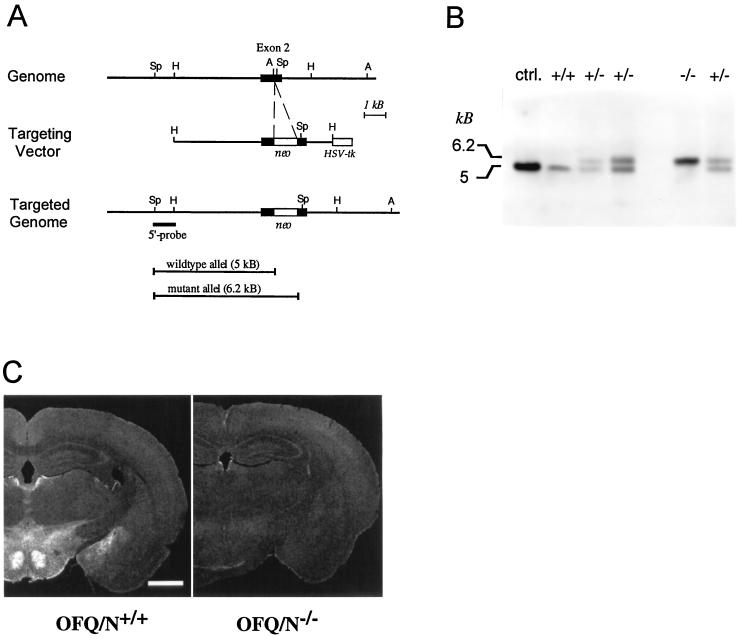
Figure 1.
Disruption of the murine orphanin FQ/nociceptin gene and analysis of expression. (A) Knockout strategy. Restriction maps of the wild-type locus (Top), the targeting construct (Middle), and the mutant gene locus (Bottom) are shown. neo, neomycin resistance; HSV-tk, herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase; restriction sites: A, ApaI; H, HindIII; Sp, SphI. Horizontal bars show SphI restriction fragments of wild-type and mutant alleles detected by the 5′ probe. (B) Southern blot analysis of SphI-digested genomic DNA from mouse-tail biopsies hybridized with a 900-bp HindIII–SphI-fragment as 5′ probe. ctrl., control DNA from untransfected E14 embryonic stem cells; genotypes: +/+, wild type; +/−, heterozygous; −/−, homozygous. (C) Immunocytochemical analysis of OFQ/N expression in OFQ/N+/+ and OFQ/N−/− mouse brains. Coronal sections at the level of the hypothalamus are shown. Intense staining can be observed in OFQ/N+/+ mice in the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, amygdala, and habenular nucleus. (Bar = 1 mm.)