Figure 1. Potential roles of heat shock proteins (HSP) in acute lung injury.
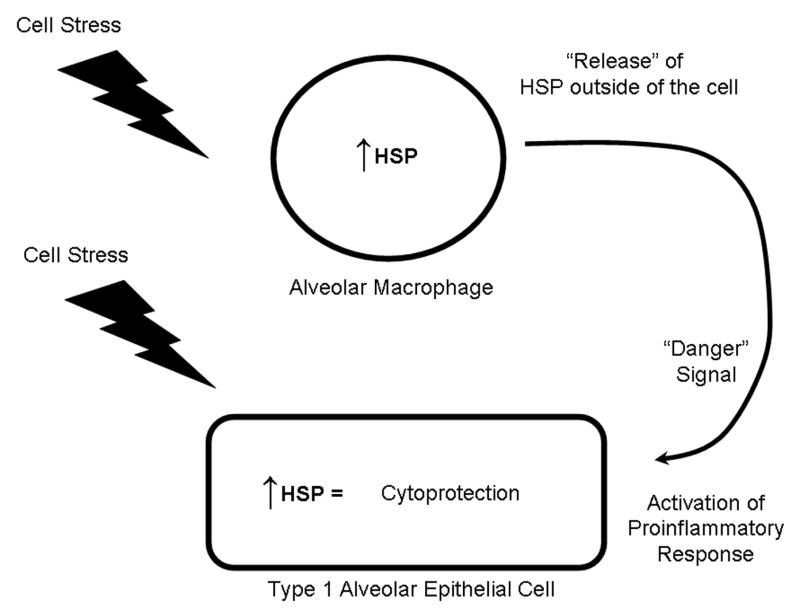
The expression of heat shock proteins in both alveolar macrophages and airway and alveolar epithelial cells is upregulated in response to a myriad of cell stressors, including LPS, free radicals, thermal stress, and hypoxia. Increased expression of heat shock proteins results in a cytoprotective response in these cell types. Release of heat shock proteins (by an as yet unidentified mechanism) may serve as a “danger signal” to activate the inflammatory response in surrounding cells.
