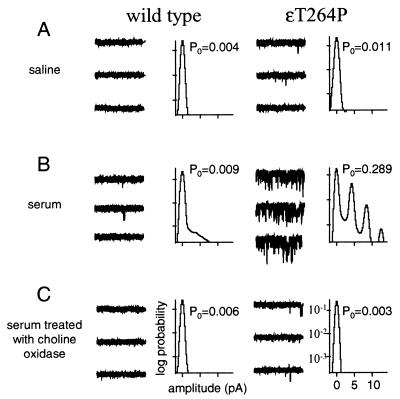
Figure 1.
Serum choline activates SCCMS mutant AChRs. Example currents (each trace is 1 sec; traces are continuous and are separated by 10 pA; inward current is down) and all-point amplitude histograms (logarithmic scale) from human AChR exposed to different solutions that did not have any exogenous agonist. Wild-type AChR rarely opens when exposed either to saline (A) or to human serum (B). The SCCMS mutant ɛT264P opens with a significant probability when exposed to serum (B). Treatment of the serum with choline oxidase eliminates this activation (C), indicating that choline is the serum component that is causing the activity.