Abstract
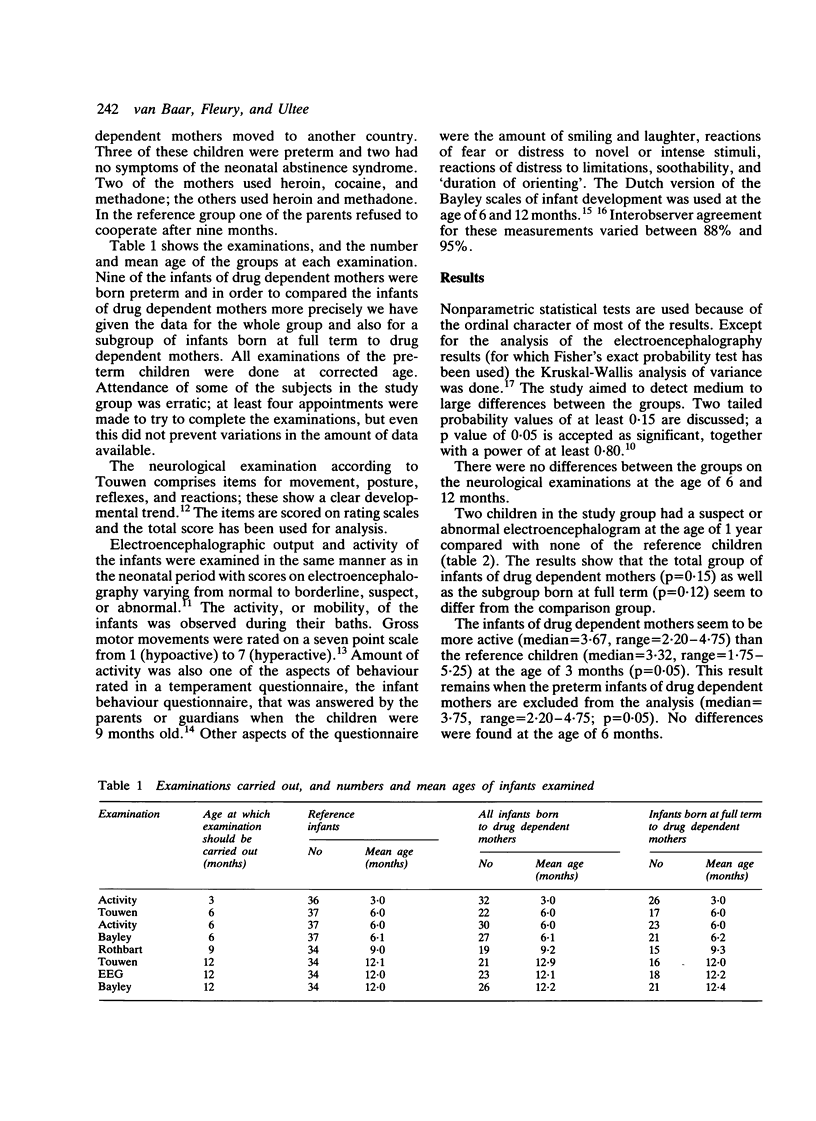
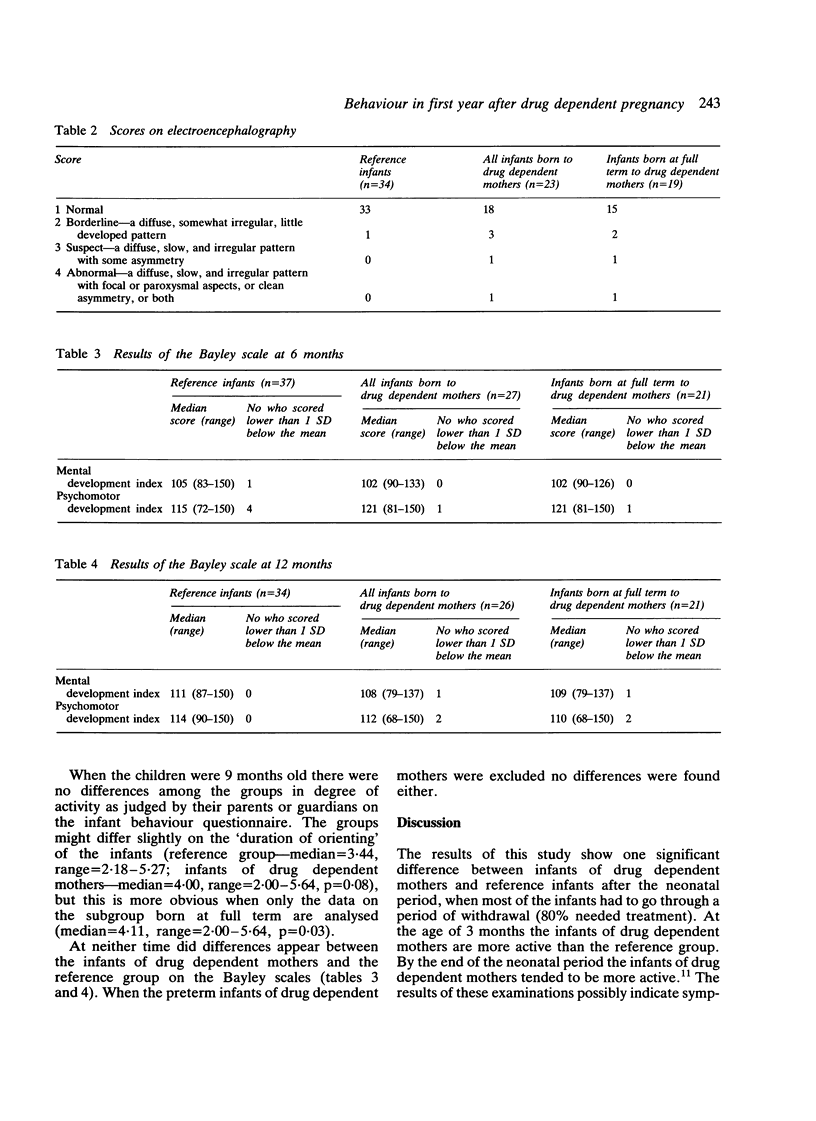
Neurobehavioural development of a group of 35 infants of drug dependent mothers and of a reference group of 37 infants was compared. Two tailed testing showed that at the age of 3 months the infants of drug dependent mothers seemed to be more active than the reference group; at 6 months, however, no difference was found. On the infant behaviour temperament questionnaire, infants of drug dependent mothers tended to have slightly better scores for 'duration of orienting' at the age of 9 months; five other dimensions of behaviour did not differ between the groups. The Bayley scales of infant development and neurological examination according to the method of Touwen did not show any significant differences among the groups at the ages of 6 or 12 months. At 12 months infants of drug dependent mothers had slightly but not significantly worse results on electroencephalography. Studied with multidisciplinary measurements, the development of infants of drug dependent mothers does not seem to diverge particularly from the development of the reference group.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aylward G. P. Methadone outcome studies: is it more than the methadone? J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):214–215. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff I. J., Burns K. A., Burns W. J., Schnoll S. H. Prenatal drug exposure: effects on neonatal and infant growth and development. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1986 Jul-Aug;8(4):357–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deren S. Children of substance abusers: a review of the literature. J Subst Abuse Treat. 1986;3(2):77–94. doi: 10.1016/0740-5472(86)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond M. M., Wilson G. S. Neonatal abstinence syndrome: Recognition and diagnosis. Addict Dis. 1975;2(1-2):113–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenbach K., Finnegan L. P. Neonatal abstinence syndrome, pharmacotherapy and developmental outcome. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1986 Jul-Aug;8(4):353–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramer C. M., Lodge A. Neonatal addiction: a two-year study. Part I. Clinical and developmental characteristics of infants of mothers on methadone maintenance. Addict Dis. 1975;2(1-2):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer H. R. Activity level as a constitutional determinant of infantile reaction to deprivation. Child Dev. 1966 Sep;37(3):595–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M. E., Reynolds K. S. Psychological characteristics and development of narcotic-addicted infants. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1983 Dec;12(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(83)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M. E., Starr R. H., Ostrea E. M., Chavez C. J., Stryker J. C. Behavioural concomitants of prenatal addiction to narcotics. J Pediatr. 1976 Nov;89(5):842–846. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. S., Desmond M. M., Wait R. B. Follow-up of methadone-treated and untreated narcotic-dependent women and their infants: health, developmental, and social implications. J Pediatr. 1981 May;98(5):716–722. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80830-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Baar A. L., Fleury P., Soepatmi S., Ultee C. A., Wesselman P. J. Neonatal behavior after drug dependent pregnancy. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Feb;64(2):235–240. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


