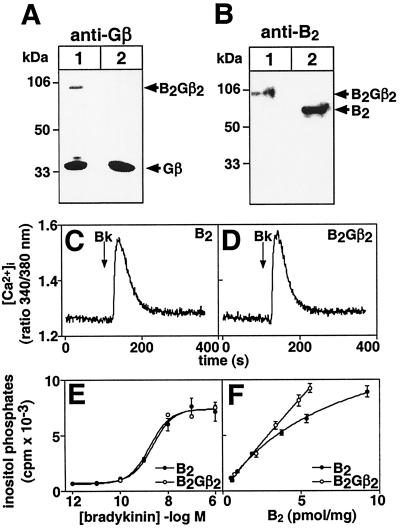
Figure 4.
Characterization of a fusion protein between the B2 receptor and the Gβ2 subunit. (A and B) Expression of the B2Gβ2-fusion protein in COS cells (lane 1). Cells transfected with the wild-type B2 receptor served as a control (lane 2). The immunoblots were analyzed with anti-Gβcommon (A) or anti-B2 receptor (B) antibodies. (C and D) Bradykinin-stimulated rise in [Ca2+]i in fura-2-loaded HEK-293 cells transfected with the wild-type B2 receptor (C) or with the B2Gβ2 fusion protein (D). At the time point indicated by an arrow, 100 nM bradykinin (Bk) was added. (E) Bradykinin-induced rise in inositol phosphate levels in COS cells transfected with the wild-type B2 receptor or with the B2Gβ2-fusion protein. Cells expressed 6.1 pmol/mg protein of wild-type and 3.9 pmol/mg protein of B2Gβ2 receptor. Data are from a representative experiment (triplicates ± SD) that was reproduced three times with similar results. (F) Inositol phosphate levels of COS cells expressing different levels of wild-type B2 receptors or of B2Gβ2 fusion protein after stimulation by 100 nM bradykinin. The amount of expressed receptors is given as pmol/mg protein. Data are from a representative experiment (triplicates ± SD) that was reproduced three times with similar results.