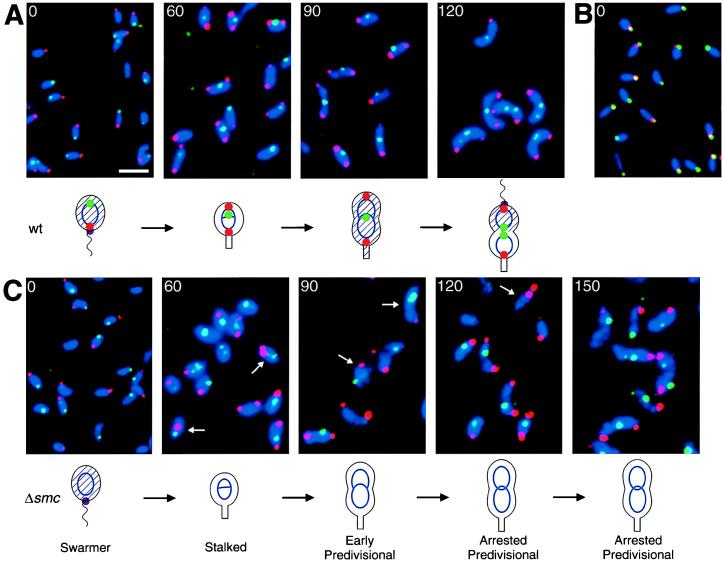
Figure 5.
Localization of the origin and terminus proximal regions of the Caulobacter chromosome by using FISH. Wild-type (A and B) and smc null mutant (C) swarmer cells were isolated and allowed to progress synchronously through the cell cycle at 32°C. At the indicated times (in minutes), the cells were fixed and hybridized simultaneously with a Cy3-labeled origin probe (red) and a FluorX-labeled terminus probe (green) (A and C). In B, the origin was localized by using a Cy3-labeled origin probe (red), and the McpA chemoreceptor was visualized by immunofluorescence staining with FITC-labeled secondary antibodies (green). The McpA protein localizes at the flagellated pole in swarmer cells (30). The nucleoids were visualized by DAPI staining (blue). Because no nucleoid-free regions are present in wild-type Caulobacter, the DAPI staining outlines the cells. Arrows indicate cells with abnormal localization of the origin or the terminus, and the white scale bar represents 2 μm. The cell cycle of each strain is diagrammed. Blue ovals and theta structures represent nonreplicating and replicating chromosomes, respectively. The intracellular localization of the origin (red dot), the terminus (green dot), and the McpA chemoreceptor (purple dot) are shown. The presence of CtrA (29) is indicated with shading of the cell.