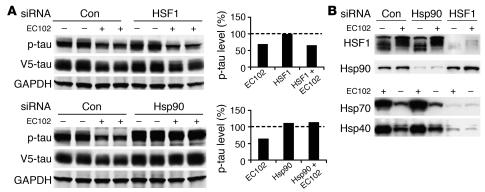
Figure 4. Reductions in p-tau by Hsp90 inhibition are primarily mediated by a constitutive, not an inducible, chaperone response.
(A) HeLa cells were transfected in duplicate with nonsilencing control, Hsp90, or HSF1 siRNA pools and incubated for 72 hours. The cells were then transfected with V5-tau and harvested after 24 hours’ EC102 exposure. EC102 caused robust reductions in p-tau and V5 immunoreactivity in cells transfected with a nonsilencing control or HSF1 siRNA (approximately 35%), while Hsp90 knockdown prevented this reduction. Densitometric values for Hsp90 and HSF1 siRNA pools are represented in separate graphs as a percentage of the optical density for nontransfected, vehicle-treated control cells after GAPDH normalization (dashed line). (B) HSF1 knockdown prevented Hsp40 and Hsp70 induction by EC102, while Hsp90 knockdown had no effect on either of these Hsps. Hsp90 levels were unaffected by HSF1 knockdown. EC102 treatment caused a shift in the distribution of HSF1 species, suggestive of phosphodependent activation.