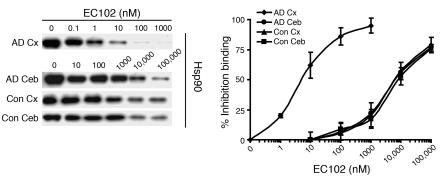
Figure 9. Hsp90 expressed in affected tissue of AD brains has significantly increased binding affinity for EC102.
Brain homogenates from affected (temporal cortex, Cx) or unaffected (cerebellar cortex, Ceb) areas of 3 AD patients’ brains and homogenates from the same areas in brains of 3 control cases were evaluated for binding affinity to Hsp90 inhibitors in a competitive binding assay using a biotin-GA probe and increasing concentrations of EC102. Hsp90 derived from the temporal cortices of each AD patient showed 1,000-fold greater binding affinity for EC102, with an IC50 of 6 ± 3.6 nM, compared with Hsp90 from the cerebella, which had an IC50 of 6,000 ± 1,000 nM (P < 0.01). Controls had an IC50 of 6,000 ± 2,000 nM and 7,333 ± 2,081 nM in the temporal and cerebellar cortices, respectively. An example of the Hsp90 levels from a case and control from each area examined following competition assay between biotin-GA and EC102. Note the similar levels of Hsp90 present at 0 μM EC102 among all tissues examined.