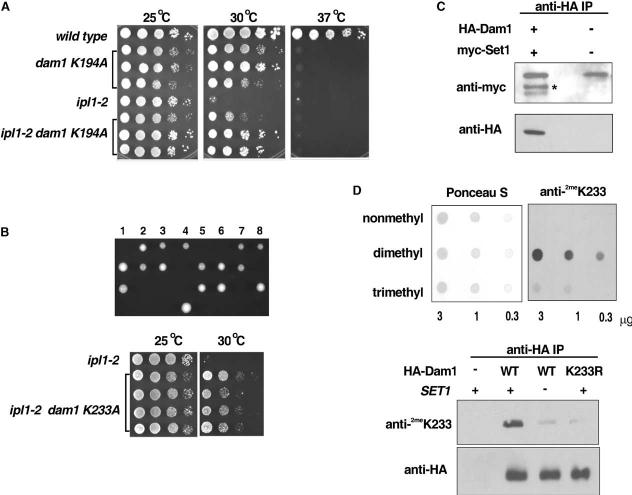
Plate spot assays (as described in previous figures) were used to compare the growth of the indicated strains. Three independent dam1 K194A colonies and three independent ipl1-2 dam1 K194A colonies are shown for comparison.
Eight independent tetrads from sporulation of dam1 K233A/DAM1 heterozygotes (upper panel). In each case, only two spores were recovered. DNA sequencing revealed that these carry the wild-type DAM1 allele (data not shown), indicating that the dam1 K233A mutation is lethal. However, plate spot growth assays (lower panel) reveal that the lethality of dam1 K233A is suppressed by ipl1-2 and also that the temperature sensitivity of ipl1-2 is suppressed by dam1 K233A.
Immunoblot of immunoprecipitates from cells expressing native or HA-tagged Dam1 with either native or myc-tagged Set1. Immunoprecipitation was performed with the anti-HA antisera and the immunoblot was probed with either an anti-myc antibody or an anti HA-antibody, as indicated. *myc-Set1.
(Upper panel) The specificity of the anti-dimethyl K233 Dam1 antisera was confirmed using a dot blot of synthetic Dam1 peptides identical in sequence but containing lysine, dimethyl-lysine, or trimethyl-lysine at the position of K233. Ponceau S staining of a sister blot is shown to confirm equal loading of the peptides. (Lower panel) Wild-type (WT) or K233R mutant HA-tagged Dam1 was immunoprecipitated from wild-type or set1 Δ cells using the anti-HA antibody. An immunoblot of the immunoprecipitates was probed with either anti-HA or the anti-dimethyl K233 Dam1 antisera, as indicated. Immunoprecipitates from a wild-type strain lacking HA-Dam1 is shown as a negative control.