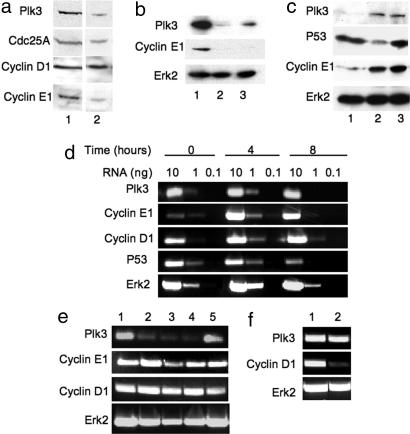
Fig. 4.
Plk3 regulates the level of cyclin E1 by a posttranscriptional mechanism. (a) Eight hours after serum addition, MCF10A cells infected with Plk3–1601 virus (lane 2) and synchronized by serum starvation show a significant reduction in cyclin E1 protein level relative to control cells 8 h after serum addition (lane 1). Levels of two other important G1 proteins, cyclin D1 and Cdc25A, were not significantly affected. (b) Cells treated with Plk3–1842 virus also showed a significant reduction in cyclin E1 at 8 h after release from serum starvation. Lanes: 1, control; 2, Plk3–1842; 3, Plk3–1601. (c) Eight hours after release from serum starvation, MCF10A cells treated with virus targeting P53 showed no effect on Plk3 or cyclin E1 levels relative to cells treated with the control virus PLK0 puro.1. Lanes: 1, Plk3–1601; 2, P53-virus; 3, control. (d) Uninfected MCF10A cells were synchronized by serum starvation, then relative message levels of Plk3 and the G1 cyclins D1 and E1 were evaluated by RT-PCR. P53 and Erk2 message levels were included for comparison. Plk3 and cyclin D1 message levels were high before serum addition, were higher at 4 h after release, and fell again by 8 h after serum addition. Cyclin E1 message was barely detectable before serum addition, peaked at 4 h, and was somewhat reduced by 8 h. P53 message showed no difference from 0–4 h but was significantly reduced at 8 h after serum addition. The message level of the constitutively expressed Erk2 is included for comparison. (e) Four hours after induction with serum, MCF10A cells treated with lentivirus-targeting Plk3 showed a significant reduction in message for Plk3 but no significant effect on message levels of cyclin E1 or cyclin D1. Erk2 message level is included for reference. Messages were amplified from 2 ng of RNA. Lanes: 1, control virus; 2, Plk3–1934; 3, Plk3–1845; 4, Plk3–1601; 5, P53-virus. (f) Plk3 message level was unaffected by virus-targeting cyclin D1, although cyclin D1 message levels were significantly reduced.