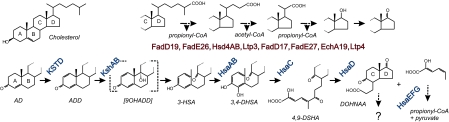
Fig. 1.
The deduced cholesterol catabolic pathway of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1, M. tuberculosis H37Rv, and M. bovis bacillus Calmette–Guérin. The enzymatic steps of side-chain degradation and ring opening are depicted. The latter are important for H37Rv survival in the macrophage (Fig. 2). Dashed arrows indicate multiple enzymatic steps. The compound in brackets undergoes nonenzymatic hydrolysis. Genes responsible for the degradation of rings C and D in RHA1 are not conserved in H37Rv or bacillus Calmette–Guérin. ADD, 1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione; 9OHADD, 9α-hydroxy-1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione; KshAB, 3-ketosteroid 9α-hydroxylase.