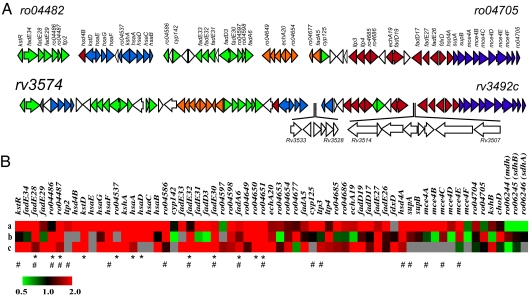
Fig. 2.
The cholesterol catabolic genes of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 and M. tuberculosis H37Rv: comparison of their organization and their activities in different studies. (A) Genes in the physical map are color-coded according to assigned function: purple, uptake; red, side-chain degradation; blue, cleavage of rings A and B; orange, degradation of the DOHNAA propionate moiety; green, degradation of rings C and D. White arrows represent genes for which no reciprocal homologue is present. The nucleotide sequences of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. bovis bacillus Calmette–Guérin clusters share 96% identity. (B) Heat map indicating correlation between gene expression (fold difference) during growth of RHA1 on cholesterol versus pyruvate (a), effect of gene disruption on H37Rv survival in IFN-γ-activated macrophages according to TraSH analysis (reciprocal of ratio) (16) (b), and gene expression in H37Rv after 48 h of growth in IFN-γ-activated macrophages (18) (c). M. tuberculosis genes predicted as essential for survival in the macrophage (16, 32) and in vivo in mice (17) are indicated by * and #, respectively.