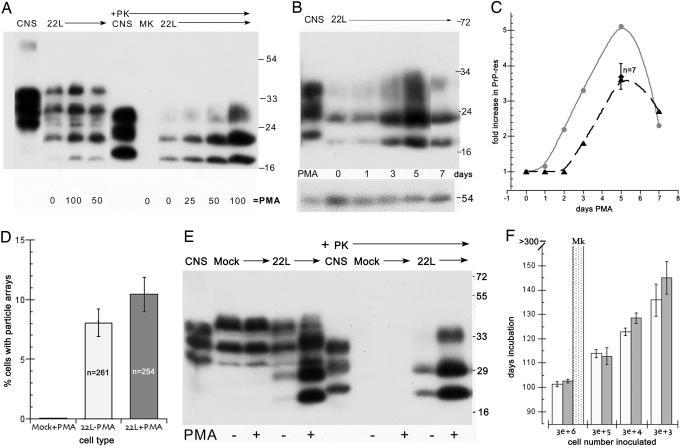
Fig. 2.
Relationship of PrP-res, virus-like particles, and infectivity in N2a + 22L cells grown with and without PMA. (A) Dose–response from 0 to 100 ng/ml PMA for 5 days of PrP and corresponding PrP-res amounts (+Pk lanes of whole-cell lysates treated with proteinase K as described in ref. 4). Note the strong increase in PrP-res at 100 ng/ml. CNS is brain homogenate control. MK are mock-infected cells and show no PrP-res. (B) PrP-res during continuous treatment with 100 ng/ml for 1–7 days shows the strongest response at 5 days; cells were treated in parallel and collected at sequential times. (C) Quantitative analysis of the increase in PrP-res in seven independent experiments with 75–100 ng/ml PMA (dotted line). Note the reproducible rise at 5 days (± SEM). The gray line shows the PMA-induced PrP-res increase versus a parallel nondrug control (see E) in cells that were tested for infectivity. (D) Count of virus-like 25-nm particle arrays in PMA-treated mock (uninfected N2a) control cells and in N2a + 22L cells without (22L-PMA) and with (22L+PMA) the drug. More than 250 cells were counted by EM for each sample, and the inclusion of any questionably positive arrays makes the percentage of positives overestimated. Nevertheless, there is no significant increase in the number of particle arrays with PMA. (E) Western blot of an aliquot of the mock-infected, untreated 22L, and PMA-treated 22L cells inoculated in mice for infectivity titrations. The mock cells show no PrP-res (+PK lanes), and the PMA-treated cells show an obvious increase in both PrP and PrP-res compared with their untreated counterparts. All cell lanes loaded with equal amounts of protein and infected CNS show brain-specific pattern (4). (F) Incubation time after inoculation of serial dilutions of N2a + 22L cell homogenates grown without PMA (white bars) and with PMA (gray bars). A shorter incubation time indicates a higher infectious titer. Mock-infected cells (dotted bar) at high concentrations elicited no clinical signs or neuropathology.