Figure 4.
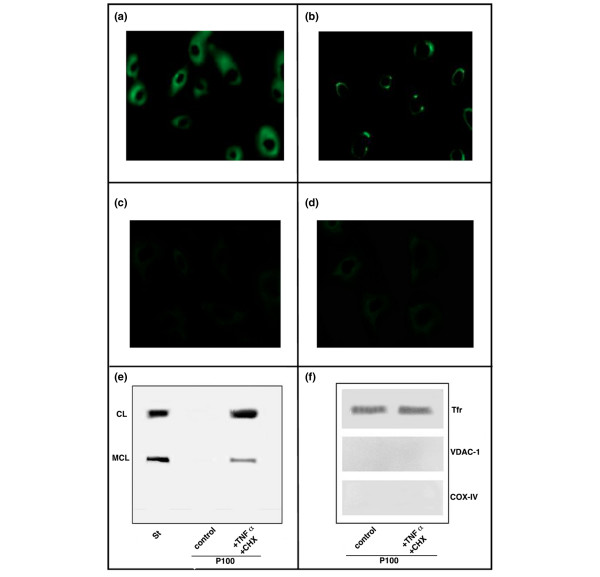
Binding of aCL antibodies and aMCL to HUVECs undergoing apoptosis. (a) Immunofluorescence of untreated HUVECs. The staining of cells with the human immunoglobulin G (IgG) fractions from antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) sera was followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody. Cells showed a fairly low and disperse immunolabelling. (b) Immunofluorescence of apoptotic HUVECs. The staining appears uneven and focalised in regions over the plasma membrane. Immunofluorescence of untreated HUVECs after previous absorption with both (c) CL and (d) MCL. The staining of cells with the human IgG fractions from APS sera was very low. Images were collected at 512 × 512 pixels, and results are representative of three repeats. (e) Light membrane pellets from either apoptotic or non-apoptotic HUVECs were analysed for phospholipid composition by thin-layer chromatography. Strong bands corresponding to CL and MCL were identified only in the membrane fractions of apoptotic HUVECs. (f) Western blot analysis of protein samples from light membranes showed strong reactivity against the membrane protein marker transferrin receptor (Tfr), with the virtual absence of mitochondrial (VDAC-1/porin and COX-IV) contaminants. CHX, cycloheximide; COX-IV, subunit IV of cytochrome c oxidase; St, standard phospholipid visualisation of lipids (cardiolipin, hydrocardiolipin, monolysocardiolipin, and dilysocardiolipin) by iodide vapours; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-alpha; VCAC-1, voltage-dependent anion channel-1.
