Figure 5. NH2-terminal charge affects the binding of chimeric TnTs to TnI and Tm.
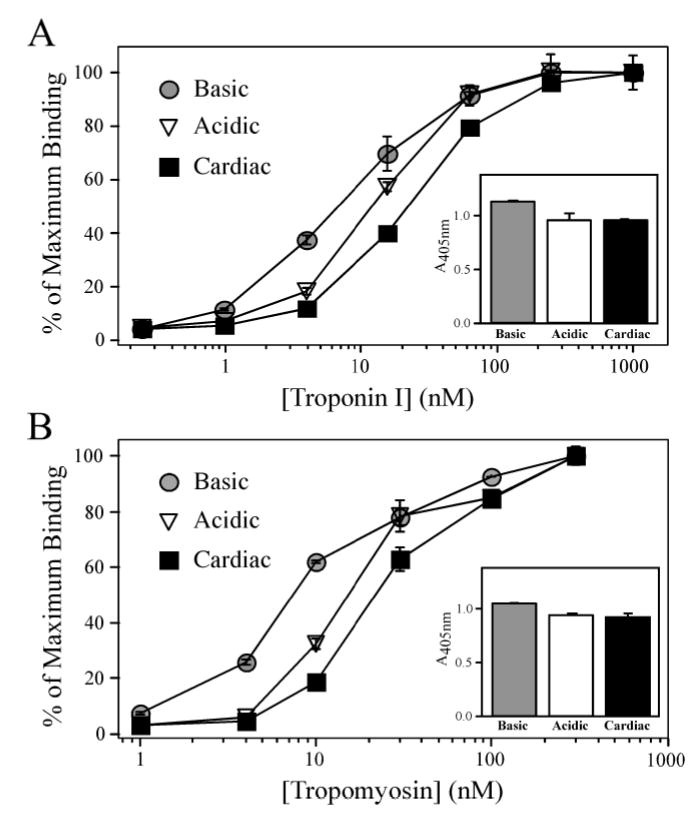
(A) Solid-phase protein binding curves demonstrate that the Basic TnT bound with higher affinity to TnI compared to that of the Acidic TnT (P < 0.05). Both Basic and Acidic chimeric TnTs exhibited higher binding affinities to TnI compared to the more acidic mouse cardiac TnT (P < 0.05). The A405nm values in the inset figure show that the Basic chimeric TnT also had a higher level of maximal binding to TnI compared to that of the Acidic chimeric TnT and mouse cardiac TnT (P < 0.05). (B) Solid-phase protein binding curves demonstrate that the Basic chimeric TnT exhibited a higher binding affinity to Tm compared to that of the Acidic chimeric TnT (P < 0.05), while the more acidic mouse cardiac TnT had the lowest binding affinity as defined by the concentration of Tm required for 50% maximum binding (P < 0.05). The A405nm values in the inset figure show that the Basic TnT exhibits a higher level of maximal binding to Tm compared to the bindings of Acidic TnT and mouse cardiac TnT (P < 0.05).
