Figure 3.
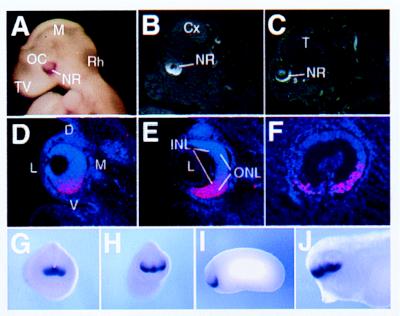
Expression pattern of vax2 in mouse (A–E), human (F), and Xenopus embryos (G–J) as determined by in situ hybridization. Vax2 expression in mouse embryos is restricted to the entire inferior neural retina, starting from E9 (A), when it is expressed in the ventral half of the optic cup, to E12.5 (B) and E16.5 (C). Eye expression in mouse at E12.5 is shown in D–E. Panels are arranged from anterior (D) to posterior (E) in coronal sections. The axis orientation of the developing eye is indicated in D: dorsal (D), ventral (V), lateral (L), and medial (M). Expression is restricted to the entire inferior neural retina, with no significant difference between inner (INL) and outer (ONL) neuroblast layers in E. (F) Sagittal section of the developing eye of a 7-week-old human embryo hybridized with the human VAX2 cDNA showing a similar pattern of expression in the ventral retina. (G–J) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing expression of Xvax2 during Xenopus development. (G) st. 18, frontal view: the gene is expressed in the anterior neural plate. (H) st. 23, frontal view: Xvax2 is expressed in ventral regions of the forebrain vesicle and in a ventral portion of the optic vesicle. (I) st. 23, lateral view: expression as in H. (J) st. 33, lateral view: expression of Xvax2 is maintained in the ventral regions of both the telencephalon and diencephalon, as well as the retina. Other abbreviations: Cx, cerebral cortex; L, lens (except in D); M, mesencephalon (except in D); Rh, rhombencephalon; NR, neural retina; OC, optic cup; T, telencephalon; and TV, telencephalic vesicle.