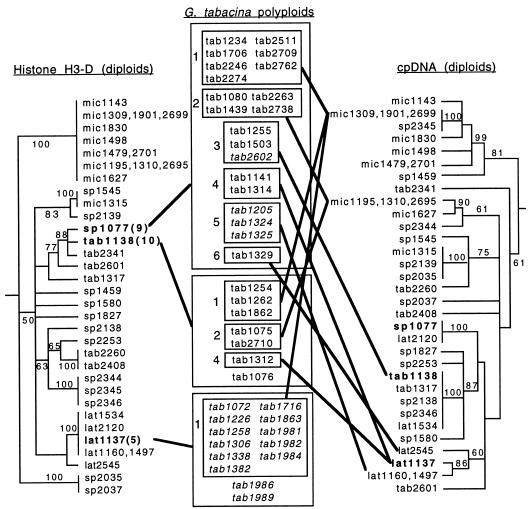
Figure 1.
Relationships of histone H3-D alleles and chloroplast haplotypes in G. tabacina polyploid accessions. Trees of histone H3-D alleles (15) and cpDNA haplotypes (11) are shown for the same set of diploid B-genome accessions. Diploid accessions having histone H3-D alleles identical to those of polyploid accessions are shown in bold type on both trees, and the allele number (classification from ref. 15) is given after the accession number on the histone tree. Polyploid accessions having these alleles are grouped in large boxes in the center column and are connected to corresponding diploid accessions by bold lines. Within these large boxes, polyploid accessions are grouped by cpDNA haplotype in smaller boxes, numbered to correspond to haplotype groups from ref. 11. These boxes are connected to diploid accessions in the cpDNA tree having the same haplotype. Polyploid accessions not in boxes possess plastome types for which no identical diploid accession has been sampled (1986, 1989) or have not been sampled for cpDNA (1076). Polyploid accessions from Pacific islands are italicized. lat, G. latifolia; mic, G. microphylla; tab, G. tabacina, sp., any of several unnamed B-genome species.