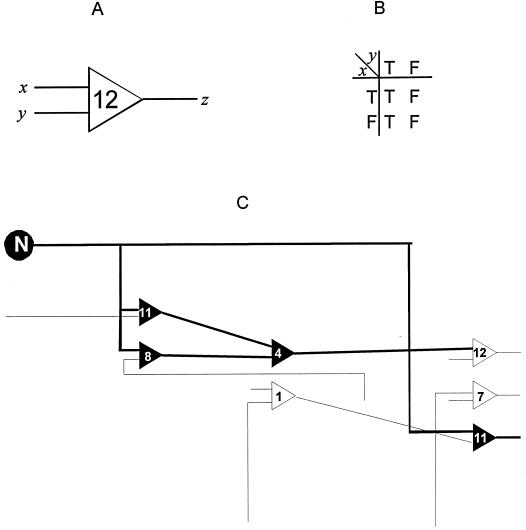
Figure 1.
(A) A Boolean circuit element. There are 16 possible element types, numbered 0–15. The Boolean function of the element is determined by interpreting its inputs (x, y) as a 2-bit binary number and using this as a pointer to a bit in the binary representation of the element number, giving the output z (0 = FALSE, 1 = TRUE). (B) Truth table describing Boolean function 12. (C) Fragment of a Boolean network, showing the propagation of injected noise information in bold. Note that the noise information is blocked at element 12, because Boolean function 12 is independent of its x input, as seen from the truth table.