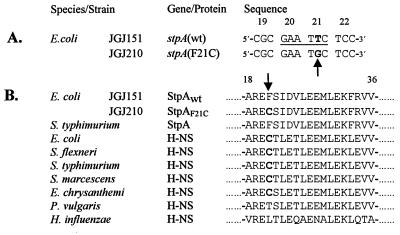
Figure 3.
Sequence analysis of the stpA gene from the Rsv mutant. (A) DNA sequence alignment of four codons, showing the single base pair difference in boldface between the stpA sequence of strain JGJ151 and the Rsv isolate JGJ210. An arrow points out the base pair substitution, and the EcoRI site in the wt sequence is underlined. The codon positions are shown above the sequences. (B) Multiple peptide sequence alignment of StpA and H-NS peptides from several species. Boldface letters highlight the cysteine residue at position 21 (also indicated by arrow). The numbers above the sequences indicate relative position, where 1 is the N-terminal methionine. Accession numbers for the protein sequences are as follows: StpA E. coli, Sw P30017; StpA Salmonella typhimurium, GB AF009363; H-NS E. coli, Sw P08936; H-NS Shigella flexneri, Sw P09120; H-NS Salmonella typhimurium, Sw P17428; H-NS Serratia marcescens, Sw P18955; H-NS Erwinia chrysanthemi EMBL X89444; H-NS Proteus vulgaris, Sw 18818; and H-NS Haemophilus influenzae, Sw P43831. EMBL, GB, and Sw refer to the European Molecular Biology Laboratory, GenBank, and Swiss-Prot databases, respectively.