TABLE 1.
Definitions and abbreviations
| AP | Action potential |
| APD | Action potential duration measured at 90% repolarization |
| BCL | Basic cycle length |
| CaV1.2 | Cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel |
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor SR Ca2+ release channel |
| CaT | Calcium transient |
| CICR | Calcium induced calcium release |
| VDI | Voltage-dependent inactivation |
| CDI | Calcium-dependent inactivation |
| ModeV | L-type Ca2+ channel states in VDI gating mode |
| ModeCa | L-type Ca2+ channel states in CDI gating mode |
| INa | Fast Na+ current, μA/μF |
| m | Activation gate of INa |
| h | Fast inactivation gate of INa |
| j | Slow inactivation gate of INa |
| ICa(L) | Ca2+ Current through L-type Ca2+ channel, μA/μF |
| ICa,Na | Na+ Current through L-type Ca2+ channel, μA/μF |
| ICa,K | K+ Current through L-type Ca2+ channel, μA/μF |
| IKr | Rapid delayed rectifier K+ current, μA/μF |
| xr | Activation gate of IKr |
| rKr | Time-independent rectification gate of IKr |
| IKs | Slow delayed rectifier K+ current, μA/μF |
| xs1 | Fast activation gate of IKs |
| xs2 | Slow activation gate of IKs |
| IK1 | Time-independent K+ current, μA/μF |
| K1 | Inactivation gate of IK1 |
| IKp | Plateau K+ current, μA/μF |
| ICa,b | Background Ca2+ current, μA/μF |
| ICa(T) | T-Type Ca2+ current, μA/μF |
| INa,b | Background Na+ current, μA/μF |
| INaCa | Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in myoplasm, μA/μF |
| INaCa,ss | Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in subspace, μA/μF |
| γINaCa | Position of energy barrier controlling voltage dependence of INaCa |
| INaK | Sodium-potassium pump, μA/μF |
| fNaK | Voltage-dependent parameter of INaK |
| σ | [Na+]o dependent factor of INaK |
| Ip,Ca | Sarcolemmal Ca2+ pump, μA/μF |
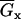 |
Maximum conductance of channel x, mS/μF |
| Km | Half-saturation concentration, mM/L |
| PS | Membrane permeability to ion S, cm/s |
| PS,A | Permeability ratio of ion S to ion A |
| γS | Activity coefficient of ion S |
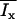 |
Maximum current carried through channel x, μA/μF |
| Vm | Transmembrane potential, mV |
| zs | Valence of ion S |
| Cm | Total cellular membrane capacitance, 1 μF |
| ACap | Capacitive membrane area, cm2 |
| AGeo | Geometric membrane area, cm2 |
| RCG | Ratio of ACap/AGeo = 2 |
| Vx | Volume of compartment x, μL |
| Δ[S]x | Change in concentration of ion S in compartment x, mM |
| CASQ2 | Calsequestrin, Ca2+ buffer in JSR |
| TRPN | Troponin, Ca2+ buffer in myoplasm |
| CMDN | Calmodulin, Ca2+ buffer in myoplasm |
| BSR | Anionic SR binding sites for Ca2+ in the subspace |
| BSL | Anionic sarcolemmal binding sites for Ca2+ in the subspace |
| SR | Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
| JSR | Junctional SR |
| NSR | Network SR |
| ss | Subspace |
| myo | Myoplasm |
| Ex | Reversal potential of current x, mV |
| [S]o | Extracellular concentration of ion S, mM |
| [S]i | Intracellular concentration of ion S, mM |
| [S]ss | Subspace concentration of ion S, mM |
| [Ca2+]JSR | Ca2+ concentration in JSR, mM |
| [Ca2+]JSR,t | Total Ca2+ concentration in JSR ([Ca2+]JSR + [csqn]), mM |
| [Ca2+]NSR | Ca2+ concentration in NSR, mM |
| Irel | Ca2+ release from JSR to subspace, mM/ms |
| adap | Function describing RyR channel adaptation |
| gradedrel | ICa(L) dependent function for determining graded response of Irel |
| vgainofrel | Function describing voltage dependence of gain |
| Iup | Ca2+ uptake from myoplasm to SR, mM/ms |
| Ileak | Ca2+ leak from NSR to myoplasm, mM/ms |
| Itr | Ca2+ transfer from NSR to JSR, mM/ms |
| τtr | Time constant of Ca2+ transfer from NSR to JSR, ms |
| Idiff | Ca2+ transfer from subspace to myoplasm, mM/ms |
| τdiff | Time constant of Ca2+ transfer from subspace to myoplasm, ms |
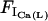 |
Ca2+ flux from ICa(L) |
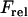 |
Ca2+ flux from Irel |
| F | Faraday constant, 96,487 C/mol |
| R | Gas constant, 8314 J/kmol/K |
| T | Temperature, 310°K |
| τ0 | Rate constant of monoexponential decay for the probability density function fit to the open probability data of the L-type Ca2+ channel |
| ICa,t | Total transmembrane Ca2+ current |
| ICa,t = ICa(L) + ICa,b + Ip,Ca − 2*INaCa − 2*INaCass | |
| INa,t | Total transmembrane Na+ current |
| INa,t = INa + INa,b+3*INaK + ICa,Na + 3*INaCa + 3*INaCass | |
| IK,t | Total transmembrane K+ current |
| IK,t = IKs + IKr + IK1 + ICa,K + IKp − 2*INaK | |
| Itot | Total transmembrane current |
| Itot = ICa,t + INa,t + IK,t | |
| Istim | Stimulus current, μA/μF |
