Fig. 9.
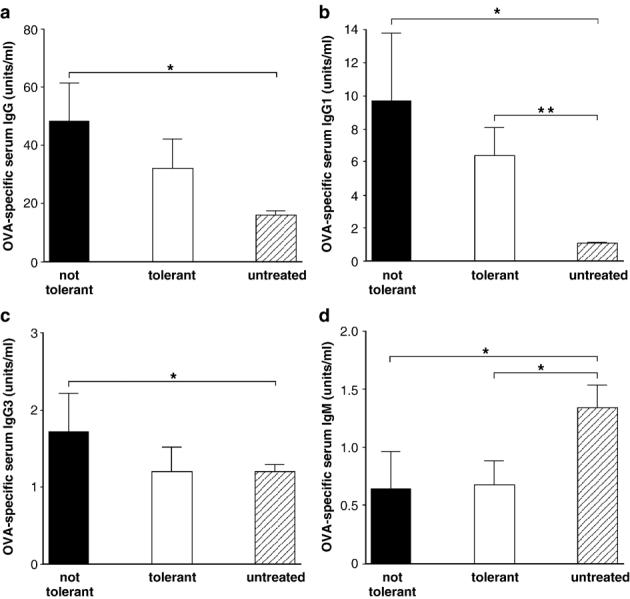
Recipients of tolerant CD4+KJ1-26+cells promote OVA-specific IgG1 but not IgG3. On day 0 BALB/c mice were injected with 2.5 × 106 CD4+ KJ1-26+ cells and, on the same day, treated with OVA and the anti-CD4/anti-CD8 mAb cocktail. All mice were boosted six and ten weeks post-priming. Three days after the last boost mice were sacrificed and spleens were removed, labeled with CD4-specific mAb and KJ1-26 and sorted to obtain a highly purified CD4+ KJ1-26+ cell population (tolerant CD4+ KJ1-26+ cells). CD4+ KJ1-26+ T cells were also sorted from untreated age and sex matched DO11.10 mice on the same day (non-tolerant CD4+ KJ1-26+ cells). A new cohort of BALB/c mice were injected with either 1 × 105 sorted tolerant CD4+ KJ1-26+ cells (n = 3) or, an equal number of non-tolerant CD4+ KJ1-26+ cells (n = 4). The level of OVA-specific IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, IgM, IgA and IgE in the serum was measured in each mouse on day 21 post-cell transfer. Data shown is the mean±SEM OVA-specific antibody at each time point and is representative of 3 experiments. * indicates statistical significance to 0.01–0.05. ** indicates statistical significance to 0.001–0.009. The Student t test was used to determine statistical significance.
