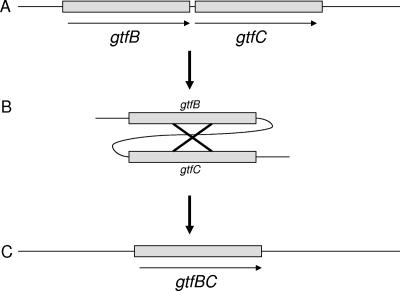
FIG. 1.
(A) The S. mutans chromosomal gtfB (4.4-kb) and gtfC (4.2-kb) genes share 98% identity over a 2,000-bp stretch (15) between the regions encoding the signal peptide and the glucan-binding domain. (B) Homologous recombination occurs at random sites within the highly homologous regions in the two genes. (C) Due to the high level of homology, the precise sites of the deletion are difficult to determine. However, the single hybrid gene that results is thought to encode the gtfB active site and the gtfC glucan-binding domain. The resulting hybrid gtfBC gene encodes a Gtf that retains enzymatic activity, though the absolute amount of activity of each clone may vary. The glucan product is more similar to that catalyzed by the gtfC product than the gtfB product.