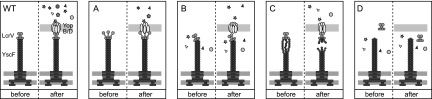
FIG. 7.
Models of proposed mechanisms for translocation-defective yscF mutations. Needle, LcrV, and translocon components are shown before and after cell contact. (WT) The needle, LcrV tip, and translocon coordinate for Yop translocation. (A) Model A. Disrupted LcrV tip assembly leads to poor translocon formation. (B) Model B. Disrupted interactions between the LcrV tip and/or the translocon leads to leakage of Yops and inefficient translocation. (C) Model C. Unstable YscF-YscF interactions lead to needle breakage before or after cell contact. (D) Model D. LcrV binding to the needle is abolished and no pores are formed. See Discussion for details.