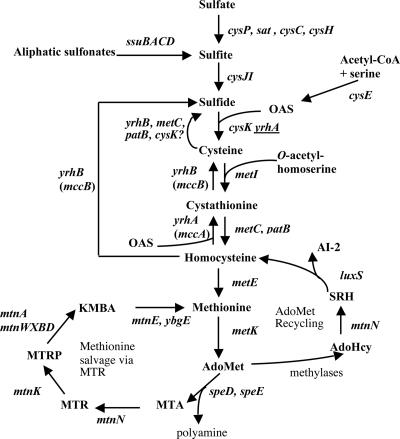
FIG. 1.
Biosynthesis and recycling pathways of sulfur containing amino acids. The enzymes present in B. subtilis are indicated by the corresponding genes: cysP, sulfate permease; sat, ATP sulfurylase; cysC, APS kinase; cysH, APS-PAPS reductase; ssuBACD, aliphatic sulfonates uptake and degradation; cysJI, sulfite reductase; cysE, serine O-acetyltransferase; cysK, OAS thiol-lyase; YrhB, MetC, PatB, and CysK have cysteine desulfhydrase activity in vitro; metI, cystathionine γ-synthase; metC and patB, cystathionine β-lyases; metE, methionine synthase; metK, AdoMet synthetase; speD, AdoMet decarboxylase; speE, spermidine synthase; mtnN, AdoHcy/MTA nucleosidase; mtnK, methylthioribose kinase, mtnA and mtnWXBD genes products are involved in the MTR-to-KMBA recycling pathway; mtnE, aminotransferase; luxS, S-ribosylhomocysteine hydrolase; yrhA (mccA), cystathionine β-synthase; yrhB (mccB), cystathionine γ-lyase and homocysteine γ-lyase. The presence of underlined yrhA indicates low OAS thiol-lyase activity in vitro for YrhA. APS, adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; KMBA, α-keto-γ-methyl-thiobutyric acid; MTA, methylthioadenosine; MTR, methylthioribose; PAPS, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; SRH, S-ribosylhomocysteine.