FIG. 7.
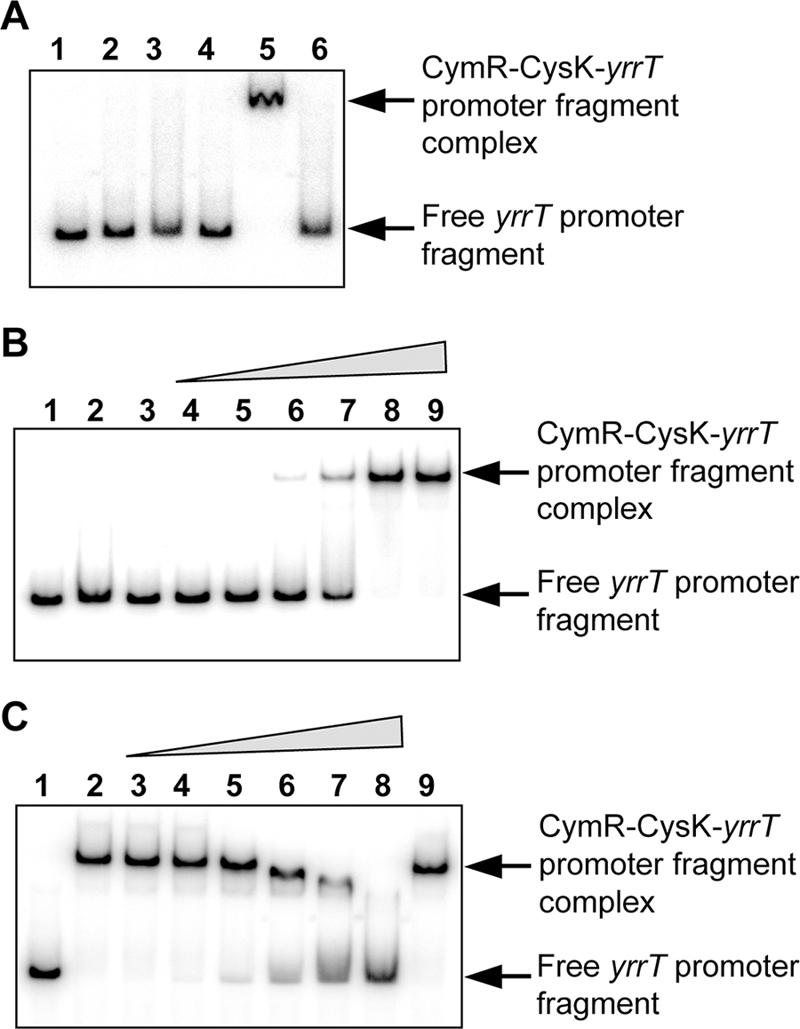
CymR- and CysK-dependent binding to the yrrT promoter region. (A) Gel mobility shift experiments were performed by incubating crude extracts of a cysK cysM double mutant of E. coli (NK3) (7.5 μg of proteins) carrying either pXT (lanes 2 and 4) or pDIA5735 (pxylA-cymR) (lanes 3, 5, and 6) with 5′-radiolabeled DNA fragments containing the yrrT promoter region. A total of 0.3 μg of purified CysK protein (lanes 4 and 5) or 0.3 μg of purified YrhA protein (lane 6) was added to the reaction mixture. Lane 1, free probe. (B) Binding of the purified CysK and CymR proteins to the yrrT promoter region. Lane 1, free probe, lane 2, 1 μg of purified CymR protein added; lane 3, 1 μg of purified CysK protein added; lanes 4 to 9, increasing amounts of CymR and CysK proteins added at a 1:1 molar ratio (50:100 ng, 75:150 ng, 100:200 ng, 150:300 ng, 200:400 ng, and 250:500 ng of CymR and CysK proteins, respectively). (C) Negative effect of OAS on the binding of the CymR-CysK complex to the yrrT promoter region. Lane 1, free probe; lanes 2 to 9, 250 ng of CymR and 500 ng of CysK. Lanes 3 to 8 show results with increasing amounts of OAS (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 mM, respectively). Lane 9, 5 mM NAS.
