FIG. 3.
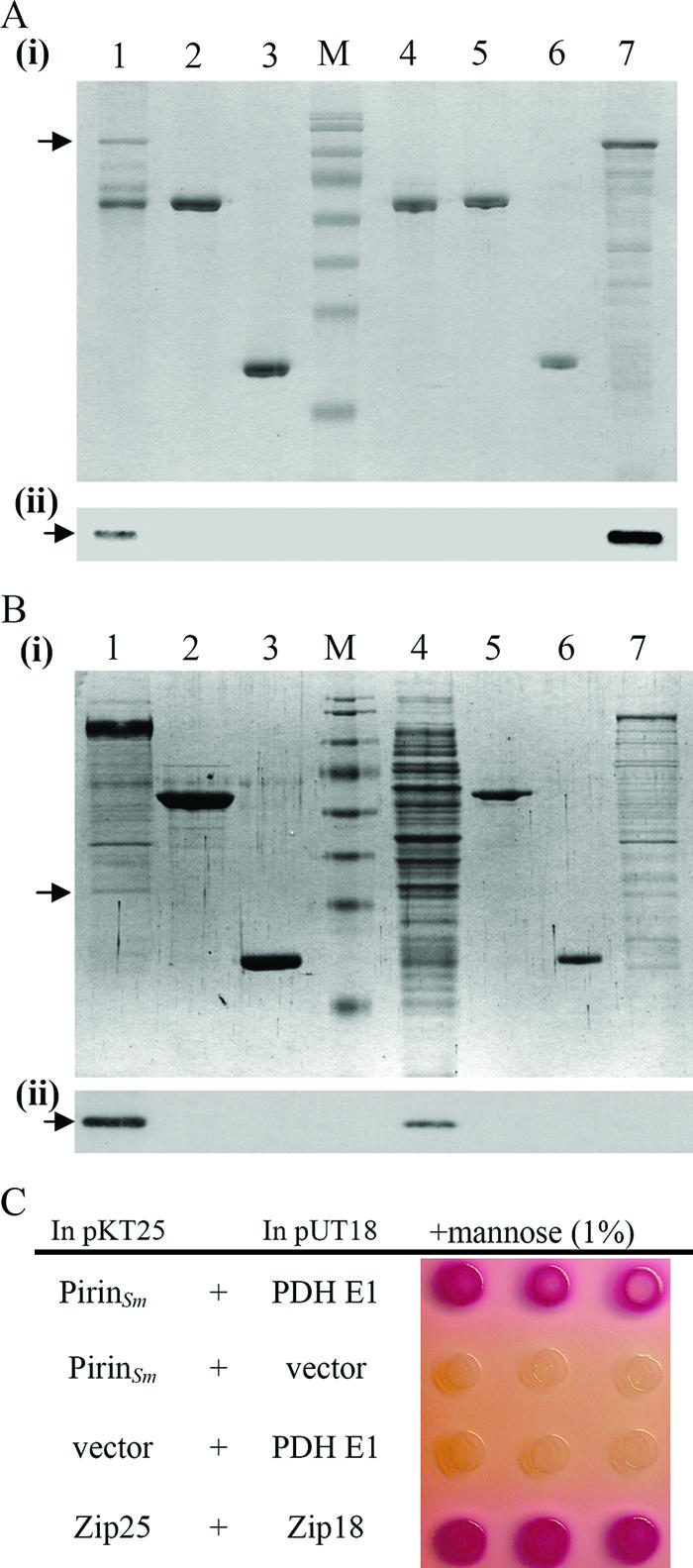
Confirmation of interaction between S. marcescens pirin and PDH E1. (A) In vitro GST pull-down assay followed by SDS-PAGE (panel i) and Western blot analysis (panel ii) using anti-His-Tag antibody was performed to confirm the interaction between GST-pirinSm and His-PDH E1. GST-pirinSm and His-PDH E1 were oversynthesized in E. coli before the assay. Lane 1, GST-pirinSm with His-PDH E1; lane 2, GST-NlpBSm with His-PDH E1; lane 3, GST Tag with His-PDH E1; lane 4, GST-pirinSm only; lane 5, GST-NlpBSm only; lane 6, GST Tag only; lane 7, E. coli(pBG20) spent crude extract containing His-PDH E1; arrow, His-PDH E1; lane M, protein markers (same as those in Fig. 2). (B) Oversynthesized GST-PDH E1 was used as the bait to confirm its interaction with pirinSm. After interaction, SDS-PAGE (panel i) and Western blot analysis using anti-pirinSm polyclonal antibody (panel ii) were performed. Lane 1, GST-PDH E1 with CH-1 lysate; lane 2, GST-NlpBSm with CH-1 lysate; lane 3, GST Tag with CH-1 lysate; lane 4, spent CH-1 cell lysate; lane 5, GST-NlpBSm only; lane 6, GST Tag protein only; lane 7, spent crude extract containing GST-PDH E1 from E. coli DH5α; arrow, pirinSm. (C) Bacterial two-hybrid assay. Colony color changed from colorless to pink-red after transformation of both pSC17 (pKT25 plasmid containing the pirinSm gene) and pSC18 (pUT18 plasmid containing the PDH E1 aceESm gene) into E. coli DHM1, indicating specific activation of maltose catabolic genes and interaction between GST-pirinSm and His-PDH E1 (14). Zip25 and Zip18 were used as positive controls.
