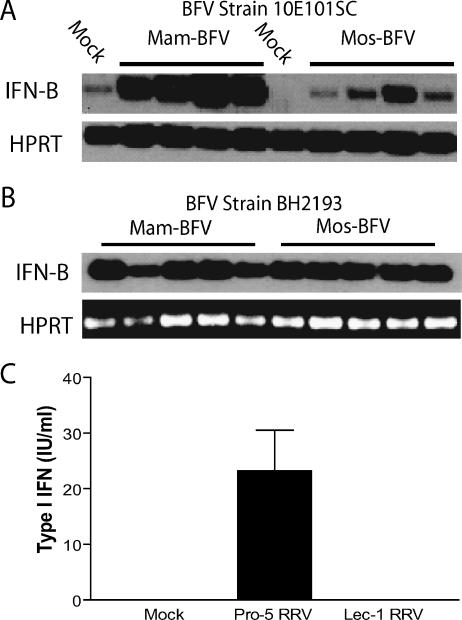
FIG. 8.
Glycosylation differences between mammalian- and mosquito-cell-derived virions of BFV and RRV contribute to differential type I IFN induction in myeloid DCs. A. Analysis of IFN induction by mam- or mos-BFV (strain 10E101SC), which has N-linked glycans on the E2 glycoprotein. mos-10E101SC BFV induced less type I IFN than mam-10E101SC BFV at 12 h postinfection as measured by RT-PCR for IFN-β transcripts. B. RT-PCR analysis for IFN-β message in mDCs following infection with BFV strain BH2193, which lacks glycosylation sites on the E2 glycoprotein. Both mos- and mam-BH2193 BVF induced IFN-β mRNA in infected mDCs. Each lane represents an independent sample. C. Virus derived from wild-type Pro-5 CHO cells (complex carbohydrates) induced more type I IFN in infected mDC cultures than virus derived from mutant Lec-1 CHO cells (high-mannose N-linked glycans) as measured by bioassay.