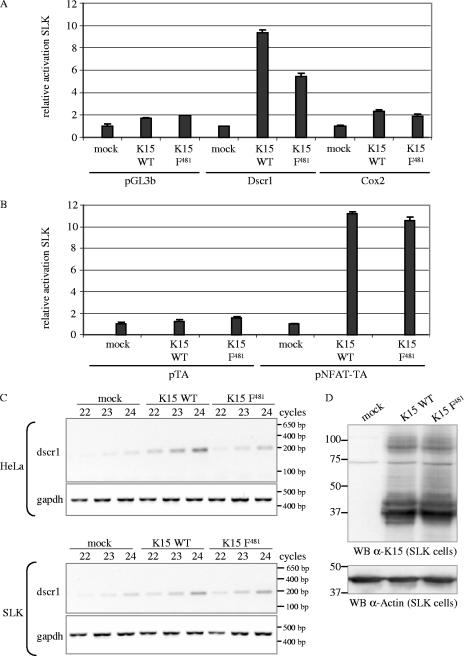
FIG. 5.
K15 activates the cox-2 and dscr1 promoter and the NFAT transcription factor in SLK endothelial cells. SLK cells were transiently cotransfected with 3 μg of K15 WT, K15 F481, or pFJ-EA (empty vector, mock) and 1 μg of reporter plasmids pGL3b (negative control), Dscr1, or Cox-2 (A) or 1 μg of reporter plasmids pTA (negative control) or pNFAT-TA (B). At 21 h posttransfection, cells were serum starved by reducing the serum concentration from 10% to 0%. At 29 h posttransfection, cells were lysed, and luciferase activities were determined. The luciferase activities are depicted as relative activity compared to mock transfections. The data are from one experiment representative of three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. Standard deviations are shown. Equal expression levels of K15 proteins were analyzed by Western blotting (data not shown). (C) Dscr1 and GAPDH semiquantitative RT-PCR. cDNA of SLK or HeLa cells transiently transfected with empty vector (mock) or K15 expression constructs K15 WT or K15 F481 was generated as described in Material and Methods. A semiquantitative PCR with 22, 23, or 24 PCR cycles was performed with dscr1-for and dscr1-rev primers amplifying a spliced transcript of 196 bp. The GAPDH PCR shows that equal amounts of cDNA were utilized for the PCR. (D) To control equal protein expression of K15 WT and K15 F481 in transiently transfected SLK cells, cells were lysed for Western blotting (WB) analysis in parallel to the cells being lysed for RNA preparation and subsequent RT-PCR analysis. K15 proteins were detected with the K15 polyclonal antibody. Blots were stripped and probed with an α-actin antibody as loading control. The transfection efficiency of SLK cells with K15 expression constructs was about 40% as judged by immunofluorescence (data not shown).