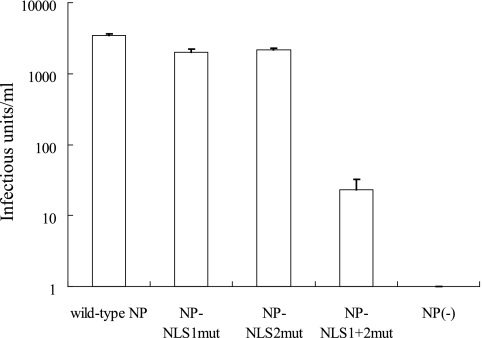
FIG. 6.
Comparison of mutant NPs' ability to support the generation of infectious VLPs. VLPs were generated with the plasmids for the expression of wild-type NP and of mutant NPs by using the plasmid-based VLP generation system previously described (21). Plasmids for the expression of wild-type NP and the indicated mutant NPs were transfected into 293T cells together with the protein expression plasmids for PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NA, M1, M2, NS1, and NS2 and pPolI-GFP (21). The culture supernatants were harvested 48 h posttransfection and mixed with helper virus (wild-type WSN virus at a multiplicity of infection of 1). MDCK cells were infected with these mixtures, and GFP-expressing cells were counted 24 h later. Error bars indicate the standard error of three independent experiments.