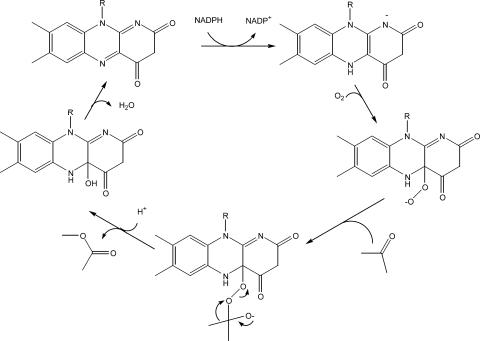
FIG. 2.
Mechanism of acetone monooxygenase AcmA, a Baeyer-Villiger-type monooxygenase. The order of substrate binding and product release is unknown; however, the reduced nicotinamide must be used to first reduce the flavin, the reduced flavin then reacts with oxygen, the peroxyflavin intermediate reacts with acetone, and a Criegee rearrangement leads to product formation.