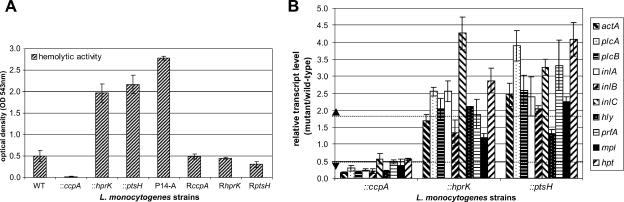
FIG. 4.
(A) Hemolytic activity of WT EGD-e, insertion mutants (::ccpA, ::hprK, and ::ptsH), revertants (RccpA, RhprK, and RptsH), and the P14-A strain (expressing constitutively active PrfA* due to a G145S exchange [52]) grown in BHI medium to an OD600 of 1.0. The hemolytic activity was determined in three independently performed experiments; the error bars indicate standard deviations of the means for the three experiments. (B) Transcriptional analysis of the virulence genes in the insertion mutants ccpA, hprK, and ptsH. The strains were grown in BHI medium to an OD600 of 1.0, and RNAs were prepared. The relative changes in the expression of the virulence genes in the mutants compared to the wild-type strain (relative transcript level of mutant/wild-type) are depicted here. The relative expression of the genes studied was normalized to the housekeeping gene rpoB as described elsewhere (43, 60). RT-PCR was performed with three independently isolated RNAs from the various strains in duplicate. The values represented here are the means of the six obtained values, and the error bars indicate the standard deviations from the means. Relative expression levels of >1.8 or <0.55 (marked by dotted line) were considered to be differentially regulated based on microarray data (for details, see Material and Methods).