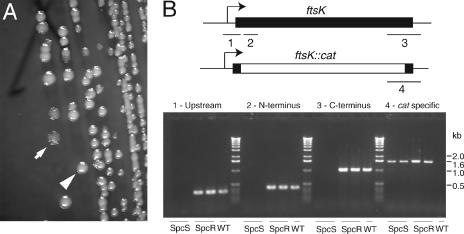
FIG. 2.
Complete loss of FtsK under FtsN overexpression conditions results in a cell division defect. (A) When JOE702 (ΔftsK Δλatt::P207-ftsN/pBAD42-ftsK) was transformed with an incompatible Kanr plasmid, grown in the presence of 0.2% arabinose, 10 μM IPTG, and 40 μg/ml kanamycin, and plated on the same medium, a mixture of wrinkled and smooth colonies was obtained. The arrow indicates a wrinkled colony. The arrowhead indicates a smooth colony. (B) PCR analysis of wrinkled (Spcs) colonies, which lost the pBAD42-ftsK(Spcr) complementing plasmid, failed to show products with primer pairs specific for ftsK (products 1, 2, and 3), consistent with plasmid loss, while yielding the expected ∼1.6-kb fragment for the ftsK::cat-Δ5 allele (product 4). Smooth (Spcr) colonies which maintained the complementing plasmid contained both the ftsK::cat-Δ5 allele and the plasmid-encoded ftsK gene. PCR analysis of wild-type cells yielded products consistent with the presence of ftsK but not with the presence of the ftsK::cat-Δ5 allele. The results for two independent colonies of each colony type are shown along with the results for a single wild-type (WT) control. PCR products are mapped on the corresponding alleles (ftsK or ftsK::cat-Δ5).