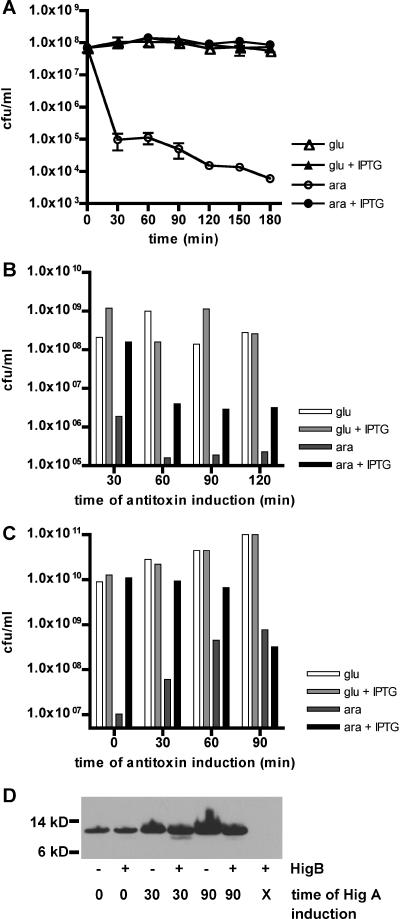
FIG. 4.
Effects of HigA production coincident with or subsequent to induction of HigB in V. cholerae and E. coli. All cultures were grown in LB medium plus 0.2% glucose, washed, and resuspended in either LB plus 0.2% glucose or LB plus 0.02% arabinose at time zero. At either time zero (A) or subsequent time points (B, C, and D), IPTG was added to some cultures to induce production of HigA (A) or HigA-Myc (B, C, and D). After further incubation, cells were plated to enumerate CFU (A, B, and C) or harvested for protein isolation and Western blotting. Results of representative experiments are shown in each panel. (A) CFU of N16961 ΔhigBA(pBADhigB/pGZHigA). (B) CFU of N16961 ΔhigBA(pBADhigB/pGZHigAmyc). (C) CFU of E. coli BW27784(pBADhigB/pGZHigAmyc). (D) Western blot of E. coli BW27784(pBADhigB/pGZHigAmyc) probed with anti-Myc antibody. Lane X, no addition of IPTG to induce HigA-Myc production.