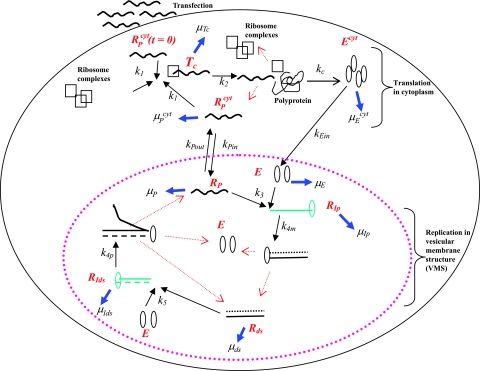
FIG. 1.
Schematic model of subgenomic HCV replication in Huh-7 cells. HCV replication starts once plus-strand RNA, RPcyt, enters the cell during transfection. The plus strand interacts with ribosome complexes to form the translation complex (Tc) with rate constant k1. Once Tc is formed, translation begins and the viral polyprotein (P) is produced at rate k2. After the polyprotein is produced, we assume the ribosome complex dissociates from Tc, leading to a free plus-strand RNA. The resulting polyprotein is cleaved with rate constant kc into separate viral proteins, including the NS5B polymerase (Ecyt) (containing RNA replicase) that is transported into the VMS at rate kEin. The plus-strand RNAs in the cytoplasm (RPcyt) are transported into VMS with rate constant kPin and out of VMS with rate constant kPout. Within the VMS, the association of plus-strand RNA (RP) and NS5B (E) result in the formation of the plus-strand replicative intermediate complex (RIp) that occurs at rate k3RP E. The complementary minus-strand RNA is then formed with rate constant k4m, and the RIp complex is dissociated to dsRNA (Rds) and NS5B polymerase (E). Finally, when dsRNA is present, the formation of the dsRNA replicative intermediate (RIds) occurs at rate k5Rds E and replicates nascent plus-strand RNA at rate k4p per complex. Once the full nascent plus RNA is replicated, the unwound plus RNA is released from the RIds complex (along with Rds and E). Ribosomes are indicated as open black squares, plus-strand RNAs are indicated as black lines, minus-strand RNAs are indicated as dotted black lines, NS5B polymerase are indicated as open black ovals, plus-strand polymerase intermediate (RIp) and dsRNA replicative intermediate (RIds) complexes are colored green. Kinetic rates k1 to k5, kPin, kPout, kc, and kEin are indicated as black arrows. Degradation rates of the NS5B polymerase (in cytoplasm [μEcyt] and in VMS [μE]), plus and dsRNA replicative-intermediate complexes (μIp and μIds, respectively), plus-strand RNAs (in cytoplasm [μPcyt] and in VMS [μP]), translation complex (μTc), and dsRNAs (μds) are indicated as blue arrows. Red arrows represent the dissociation of the replicative-intermediate complexes (RIp and RIds) and translation complexes (Tc) immediately after the full synthesis of the nascent RNA strands and viral polyprotein is finished. The vesicular-membrane structures observed in Huh-7 cells (15, 22), are represented here by just one VMS marked with a large dotted pink oval. The VMS size is not drawn to scale in relation to the Huh-7 cell.