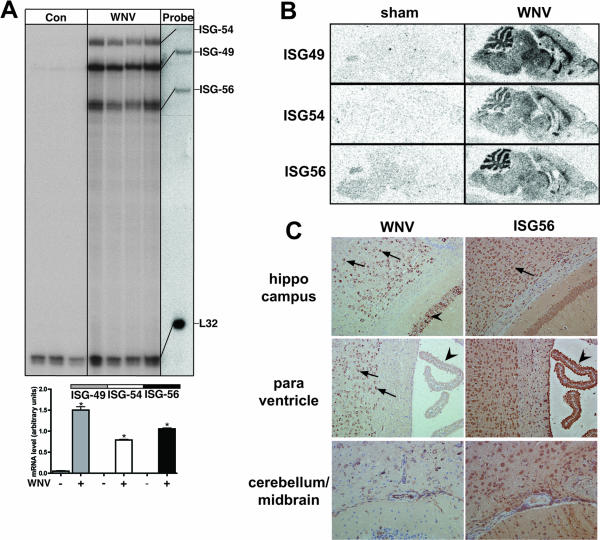
FIG. 6.
Regulation of ISG-49, ISG-54, and ISG-56 mRNA and ISG-56 protein in the brains of WNV-infected WT mice. Mice were inoculated intranasally with vehicle or vehicle plus 6 × 104 PFU of WNV (Sarafend strain). At day 7 postinfection, mice were euthanized and the brains were removed and analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. (A) RNase protection analysis revealed that compared with sham-inoculated controls the levels of ISG-49, ISG-54, and ISG-56 mRNA transcripts increased significantly (*, P < 0.05) in WNV infection. (B) Anatomic localization of ISG RNA transcripts in the brain by in situ hybridization. Compared with sham-inoculated controls, during WNV infection the levels of all three ISG RNAs increased markedly and were distributed widely throughout the brain. (C) Immunohistochemical localization of the WNV nonstructural protein NS1 compared with the ISG-56 protein. Infection of many neurons by WNV is evident in most regions of the cerebrum but was largely absent from the choroid plexus (left middle panel, arrows) and cerebellar neurons. ISG-56 protein was found to be more widespread in the majority of neurons in both cerebrum and cerebellum, as well as in the choroid plexus (right middle panel, arrowhead). Total magnification, ×100.