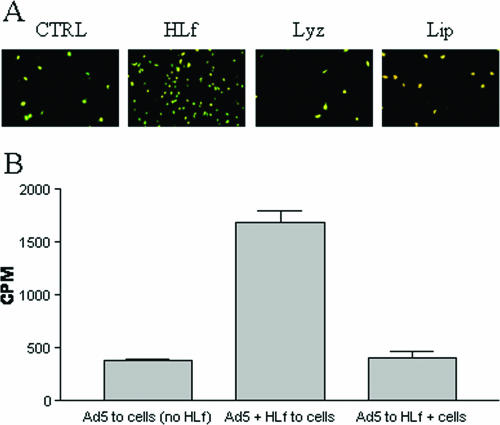
FIG. 2.
HLf promotes infection and binding of Ad5 to HCE cells. (A) HLf, but not lysozyme or lipophilin, promotes infection by Ad5 in HCE cells. Ad5 virions were preincubated with or without HLf, lysozyme, or lipophilin (6 μg/ml) and allowed to infect cells. Forty-four hours postinfection, the cells were fixed, stained, and analyzed in a fluorescence microscope. (B) Free, but not cell-associated, HLf promotes binding of Ad5 virions to HCE cells. HLf (100 μg/ml) was first preincubated with 35S-labeled virions and then incubated with cells (Ad5 + HLf to cells), or HLf (100 μg/ml) was first preincubated with cells and then with virions (Ad5 to HLf + cells). As a control, 35S-labeled virions was incubated directly with cells in the absence of HLf [Ad5 to cells (no HLf)]. After removal of unbound virions from cells by washing, the cell-associated radioactivity was quantified with a beta counter. The data are normalized with respect to the possible effect of aggregation (see Materials and Methods). For panel B, the data shown are the results of three independent experiments, and each experiment was performed in duplicate.