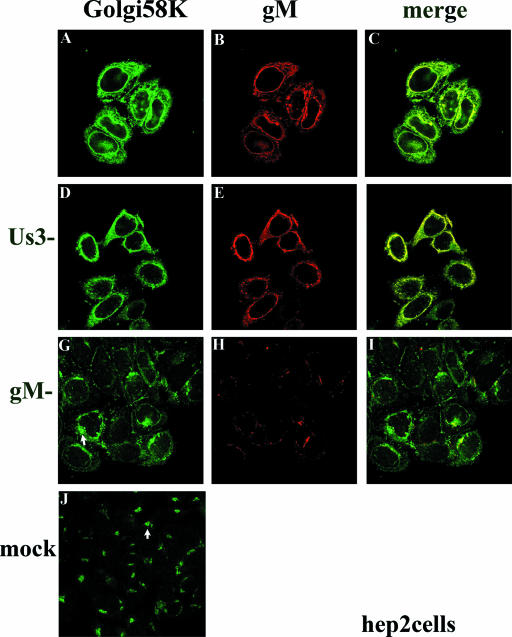
FIG. 2.
Indirect immunofluorescence of gM and Golgi localization in HEp-2 cells infected with wild type (top row), gM-null, or US3-null viruses at 16 h postinfection. HEp-2 cells were infected with the indicated viruses and were reacted with antibody to gM and mouse monoclonal antibody to Golgi 58K, a resident protein of the Golgi apparatus. Bound immunoglobulins were revealed by reaction with FITC conjugated goat anti-rabbit or Texas Red-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G followed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. Single optical sections are shown. Both the red channel and the green channel were scanned independently with only the fluorescence-stimulating laser powered on. The rightmost column shows scanned images of the left columns merged by using Adobe Photoshop software; a yellow color indicates regions where the two antibodies coincide. The arrows in panels G and J indicate different staining patterns of the Golgi marker in cells that were infected with the gM-null virus and mock infected, respectively.