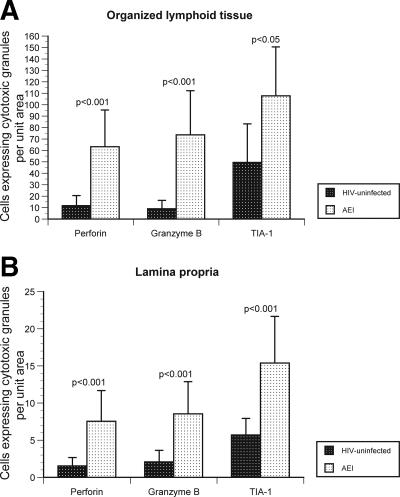
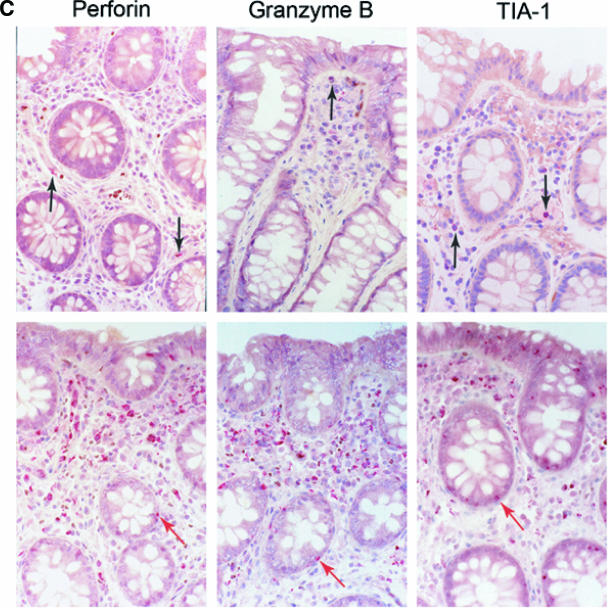
FIG. 5.
Significant increase in the cytotoxic granules perforin, granzyme B, and TIA-1 in the GI tract during AEI. (A and B) Cells expressing cytotoxic granules perforin, granzyme B, and TIA-1 (represented on the x axis) per unit area (shown on the y axis) were examined by immunohistochemistry within mucosal inductive (Fig. 5A) and effector (Fig. 5B) sites in HIV-uninfected controls and AEI subjects. (C) Panel I depicts representative sections from an HIV-uninfected control showing the few cytotoxic granule-positive cells (black arrows). Original magnification, ×100. Panel II shows representative biopsy sections from a subject with AEI depicting abundant cells expressing perforin, granzyme B, and TIA-1 in the GI lamina propria. Red arrows indicate intraepithelial cells expressing perforin, granzyme B, and TIA-1, respectively. Original magnification, ×100.