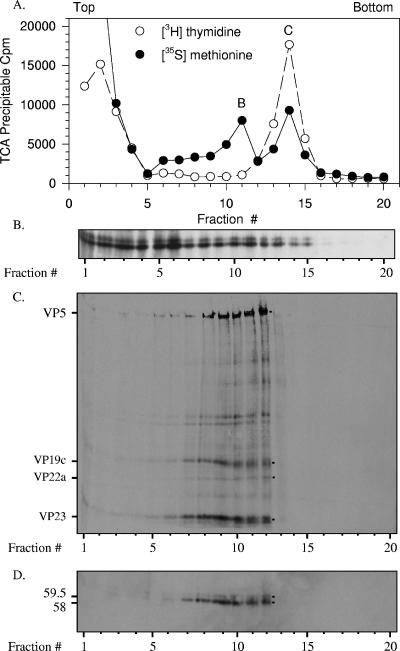
FIG. 6.
Both 59.5-kDa and 58-kDa Vhs polypeptides bind intranuclear B and C capsids. Vero cells were infected with 20 PFU/cell of wild-type HSV-1 and incubated from 4 to 18 h after infection in MEM containing [35S]methionine and [3H]thymidine to label protein and DNA, respectively. A nuclear lysate was prepared and analyzed by sedimentation through a gradient of 20 to 50% sucrose prepared in TNE. Aliquots of each gradient fraction were analyzed to determine the amounts of [35S]methionine and [3H]thymidine incorporated into TCA-precipitable material (A) and by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect the 59.5-kDa and 58-kDa Vhs polypeptides (B). The peak centered at fraction 11 was presumed to be B capsids, and that at fraction 14 was presumed to be C capsids. The putative B capsids were pelleted from fraction 11 of the first gradient, resuspended in TNE, and resedimented through a second 20 to 50% sucrose gradients. An aliquot from each fraction of the second gradient was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the resolved proteins were blotted onto an Immobilon P membrane. The membrane was subjected to autoradiography (C) to detect all 35S-labeled proteins and probed with Vhs-specific antiserum (D) to allow immunologic detection of the Vhs polypeptides. The locations of major capsid proteins are shown by dots to the right of lane 12 of panel C and labeled to the left of lane 1 of panel C. The 59.5-kDa and 58-kDa Vhs polypeptides are indicated by dots to the right of lane 12 of panel D and labeled to the left of lane 1 of panel D. In this and other figures, the smallest of the major capsid proteins, VP26, was run off the end of the gel. This was necessary in order to run the gel long enough to resolve the 58-kDa and 59.5-kDa forms of Vhs.