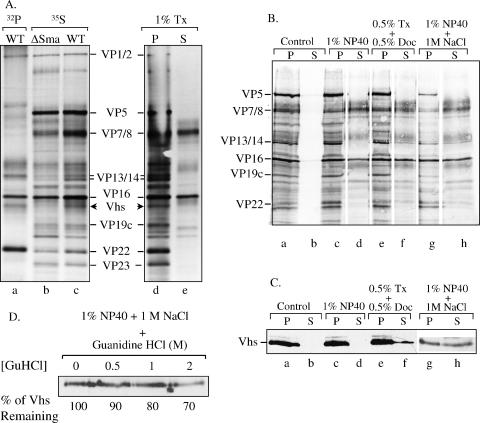
FIG. 9.
Extraction of virions with detergents, salt, and GuHCl. (A) [32P]orthophosphate-labeled wild-type (WT) virions (lane a) and [35S]methionine-labeled wild-type (lanes c to e) and Vhs-ΔSma (lane b) virions were extracted with 1% Triton X-100 (Tx) and separated into pellet (P) (lane d) and supernatant (S) (lane e) fractions as described in the text or were left untreated (lanes a to c). The various virions and fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Various virion polypeptides are labeled between lanes c and d. The wild-type Vhs polypeptide is indicated by arrowheads to the right of lane c and left of lane d. The Vhs polypeptide is missing from Vhs-ΔSma virions. (B) [35S]methionine-labeled wild-type virions were extracted for 1 h with the following buffers as described in the text: (i) 10 mM Tris (pH 7.5) (control), (ii) 1% NP-40, (iii) 0.5% Triton X-100 plus 0.5% sodium deoxycholate (Doc), and (iv) 1% NP-40 plus 1 M NaCl. The extracted virions were separated by centrifugation into a capsid-containing pellet and a supernatant. Proteins in the various fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to an Immobilon P membrane, and visualized by autoradiography to detect all virion proteins. (C) The same membrane was then probed using UL41-specific antiserum to detect the Vhs polypeptide. (D) Wild-type virions were extracted with 1% NP-40 plus 1 M NaCl, after which the capsids were pelleted. The capsids, retaining approximately 50% of the Vhs protein, were washed further with TNE containing 0 M, 0.5 M, 1 M, or 2 M GuHCl. The washed capsids were pelleted through a cushion of 25% sucrose, resuspended, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect the Vhs polypeptide. The amount of Vhs remaining bound to capsids washed with various concentrations of GuHCl was quantified by densitometric scanning and expressed as a percentage of the amount bound to TNE-washed capsids.