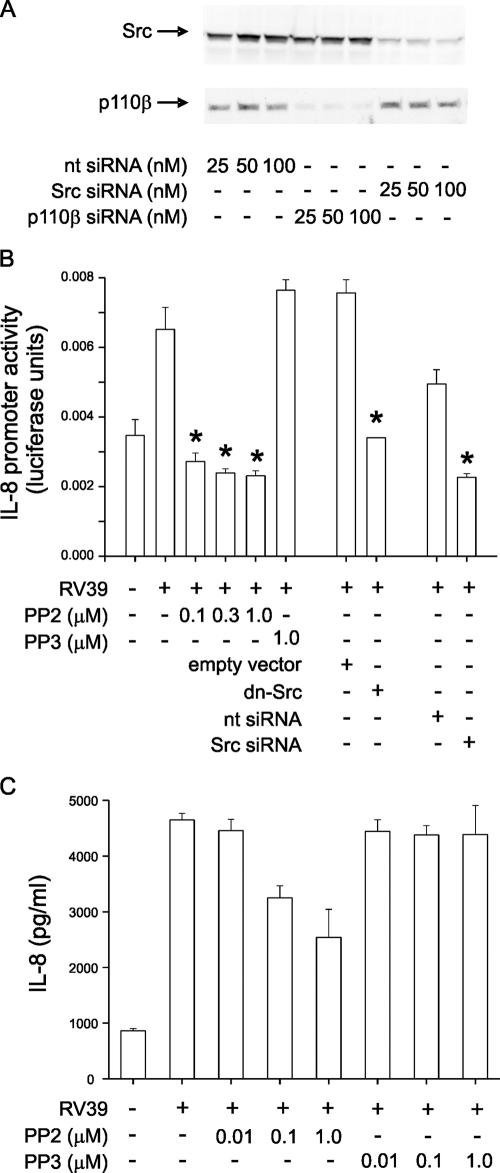
FIG. 6.
Inhibition of Src kinase activity blocks the IL-8 response to RV39. (A) Immunoblots showing knockdown of Src and p110β PI 3-kinase with specific siRNAs. (B) 16HBE14o− cells were transiently transfected with an IL-8 luciferase reporter and either 100 ng empty vector, dominant-negative K297R Src (dnSrc), 100 nM nontargeting RNA (nt siRNA), or Src siRNA. Dominant-negative Src inhibited RV39-induced IL-8 promoter activity. Selected cells were also treated either with dimethyl sulfoxide carrier, with the indicated concentration of Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP2, or with its less potent and specific analog PP3. Cells were infected with RV39 (MOI of 1 for 1 h), incubated for 24 h, and harvested for assessment of luciferase activity. (C) Primary mucociliary differentiated human airway epithelial cells were infected with 5 × 106 TCID50/ml RV39 for 1 h in the presence of either PP2 or PP3 and incubated for an additional 48 h. IL-8 protein abundance was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for 48 h. Protein abundance was inhibited by PP2 but not by a comparable concentration of PP3. For each panel, results from three experiments are shown, data shown are means ± standard errors of the means, and asterisks indicate P values of <0.05 versus those for RV39, RV39 plus empty vector, or RV39 plus nontargeting siRNA by ANOVA.