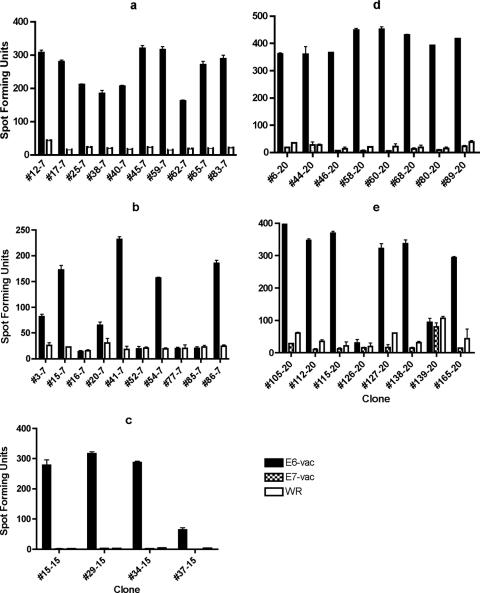
FIG. 1.
ELISPOT assays performed using E6-vac-, E7-vac-, and/or Western Reserve (WR)-infected autologous EBV LCLs as antigen-presenting cells revealed that the T-cell clones from subjects 7, 15, and 20 recognize endogenously processed E6 epitopes. The number after the hyphen indicates subject of origin. The bars represent standard errors of the means. (a) Twenty of 20 T-cell clones from the subject 7 screen positive for the E6 16-40 region were positive for an endogenously processed E6 epitope. Ten representative clones are shown. The experiment was done with an MOI of 5 in triplicates, and E6-vac and WR were tested. (b) Six of 10 T-cell clones from the subject 7 screen positive for the E6 46-70 region were positive for a endogenously processed E6 epitope. The experiment was done with an MOI of 5 in triplicates, and E6-vac and WR were tested. (c) Ten of 14 T-cell clones from the subject 15 screen positive for the E6 16-40 region were positive for a endogenously processed E6 epitope. Four representative clones are shown. The experiment was done with an MOI of 10 in duplicates, and E6-vac, E7-vac, and WR were tested. (d) Eight of eight T-cell clones from the subject 20 screen positive for the E6 16-40 region were positive for an endogenously processed E6 epitope. The experiment was done with an MOI of 5 in duplicates, and E6-vac, E7-vac, and WR were tested. (e) Six of eight T-cell clones from the subject 20 screen positive for the E6 31-55 region were positive for an endogenously processed E6 epitope. The experiment was done with an MOI of 5 in duplicates, and E6-vac, E7-vac, and WR were tested.