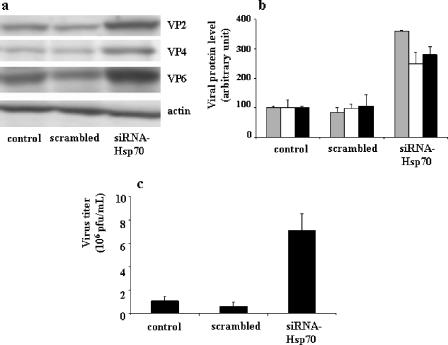
FIG. 5.
Effects of siRNA-Hsp70 transfection on rotavirus protein level (a and b) and on progeny virus production (c) in infected Caco-2 cells. (a) A cell suspension of 5 × 105 Caco-2 cells was supplied with 2 μg of siRNA-Hsp70 and then electroporated. Transfected cells were infected with rotavirus strain RF (1 PFU/cell) for 6 h as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were harvested, and lysates were subjected to immunoblotting using monoclonal anti-VP4 (clone 7.7) and anti-VP6 (clone RV133) as described in Materials and Methods. A representative experiment of four total experiments is shown. (b) Quantitative analysis of VP2, VP4, and VP6 levels in siRNA-transfected cells. Caco-2 cells were treated as described for panel a and subjected to immunoblot analysis (a representative experiment of four total experiments is displayed). VP2 (gray histograms), VP4 (white histograms), and VP6 (black histograms) were measured. (c) Quantification of virus production by siRNA-transfected and infected Caco-2 cells. Caco-2 cells were treated as described for panel a (1 PFU/cell, 18-h infection). Supernatants were titrated by a standard plaque assay with MA104 cells, as described in Materials and Methods (22). Results are expressed as PFU/ml and represent means ± SEM for six experiments. Note that in siRNA-transfected Caco-2 cells, the levels of virus structural proteins (VP2, VP4, and VP6) were significantly increased and associated with an increase of virus production.