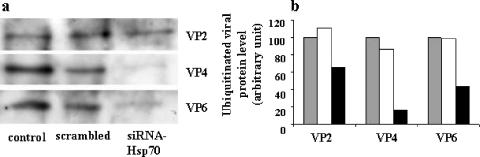
FIG. 7.
siRNA-Hsp70 effect on virus protein ubiquitination in infected Caco-2 cells. (a) A cell suspension of 5 × 105 Caco-2 cells was supplied with 2 μg of siRNA-Hsp70 and then electroporated. Transfected cells were infected with rotavirus strain RF (1 PFU/cell) for 18 h as described in Materials and Methods. Infected lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-ubiquitin antibodies, as described in Materials and Methods. Immunopurified ubiquitinated proteins were subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-VP2, -VP4, and -VP6 antibodies as described in Materials and Methods. (b) Quantitative analysis of ubiquitin-labeled VP2, VP4, and VP6 levels in siRNA-transfected and rotavirus-infected Caco-2 cells. Caco-2 cells were treated as described for panel a, and the amounts of ubiquitinated VP2, VP4, and VP6 were quantified using immunoblot scanning. Control (gray histograms), scrambled siRNA-treated (white histograms), and siRNA-Hsp70-treated (black histograms) cells were studied. Note that the decrease in expression level of Hsp70 in Caco-2 cells results in a significant decrease of the ubiquitination of virus structural proteins.