FIG. 6.
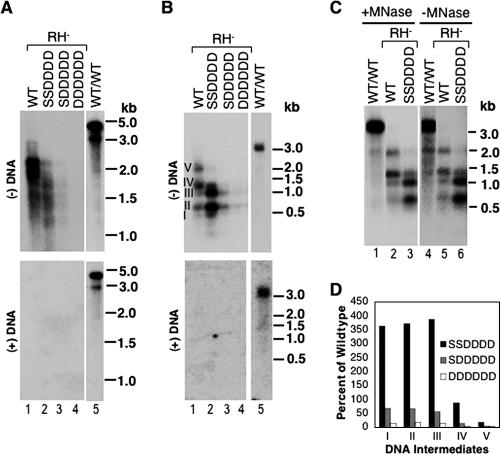
Effects of core mutations on minus-strand DNA synthesis in RNase H-defective NCs. Viral core DNA was isolated from transfected LMH cells as described in the legend to Fig. 2, except that the core-defective DHBV genome also harbored a mutant polymerase defective in RNase H activity (DHBV/C−/RH−). DNAs were extracted with (A, B, and C, lanes 1 to 3) or without (C, lanes 4 to 6) exogenous micrococcal nuclease (MNase) digestion and analyzed by Southern hybridization, with (B and C) or without (A) prior heat denaturation. Minus-strand DNA was detected using a radiolabeled riboprobe specific for the 5′ end of the minus strand (as in Fig. 5C), and plus-strand DNA was detected using a full-length riboprobe. The marker DNA sizes (kb), either DS (A) or denatured SS (B and C), are indicated. The numerals I through V in panel B refer to minus-strand DNA intermediates with increasing lengths. Lanes 5 in panels A and B and lanes 1 and 4 in panel C show the DNA synthesized by the WT polymerase in the context of the WT NC (WT/WT), as a control. (D) Relative amounts of minus-strand intermediates, designated I through V as in panel B, are expressed as percentages of those in the WT. Note that all comparisons in panel D were made among NCs that shared the same RNase H mutation.