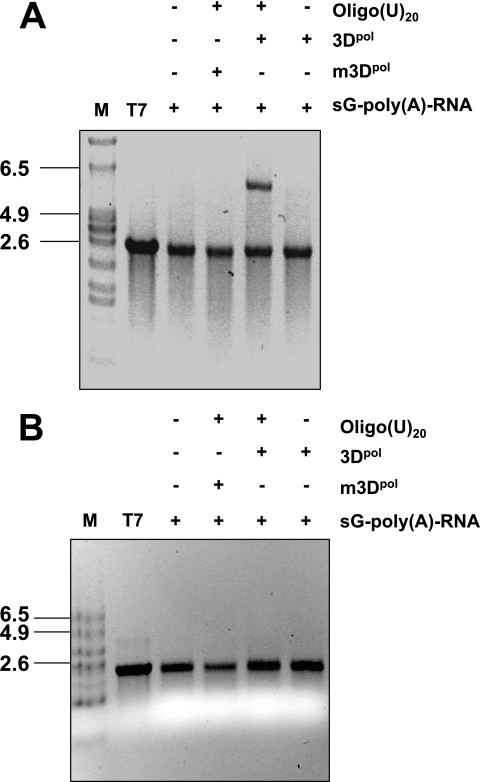
FIG. 6.
RNA synthesis by sapovirus 3Dpol. (A) RNA synthesis was examined in the presence of a synthetic subgenomic polyadenylated RNA [sG-poly(A)-RNA] used as a template in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 3 μM oligo(U)20 RNA-primer and in the presence of wild-type sapovirus 3Dpol (3Dpol) or an active site 3Dpol mutant (m3Dpol, YGD343GD344G), as indicated. Reaction products were analyzed on a nondenaturing agarose gel and visualized by UV transillumination after ethidium bromide staining. In the reaction using m3Dpol instead of wild-type 3Dpol, or omitting the addition of oligo(U)20 RNA-primer, the residual band observed corresponds to the synthetic subgenomic RNA template used in the reaction. T7, synthetic subgenomic RNA generated by T7-mediated in vitro transcription; M, RNA molecular mass marker. (B) Strand separation analysis of the reaction product of in vitro RNA synthesis by sapovirus 3Dpol. The reaction product was generated from RNA synthesis by sapovirus 3Dpol (3Dpol) from a synthetic subgenomic polyadenylated RNA [sG-poly(A)-RNA] used as a template, as indicated. Reaction products were visualized on denaturing formaldehyde-agarose gels. T7, synthetic subgenomic polyadenylated RNA generated by T7-mediated in vitro transcription; M, RNA molecular mass marker.