Figure 5.
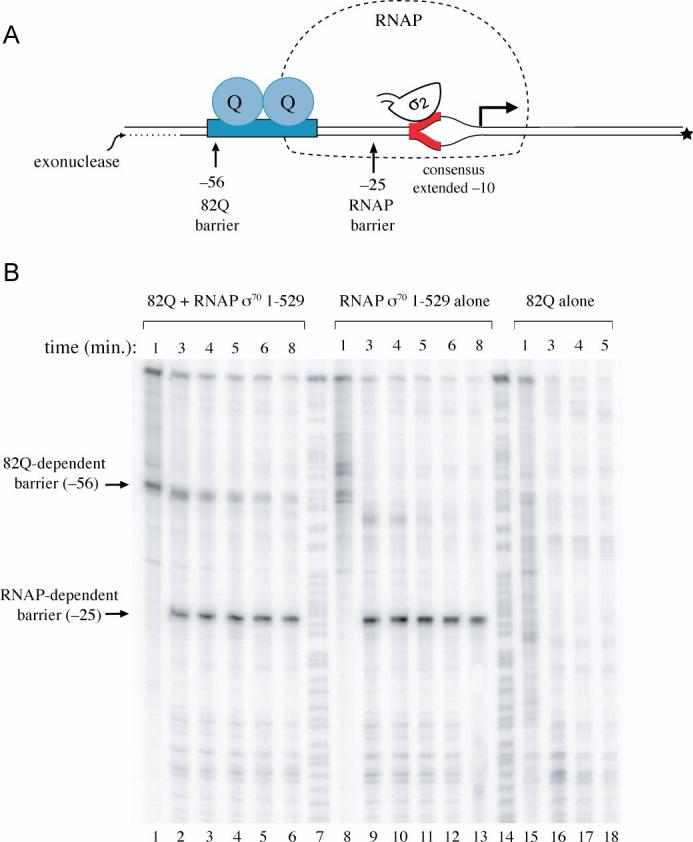
- Schematic of template used for exonuclease III challenge assay. Depicted is the 82Q-engaged transcription initiation complex lacking σ70 region 4. The modified phage 82 PR' template used in the assays is end labeled at the 5′ end of the template (bottom) strand, as indicated. Also indicated are the positions (relative to the transcription start site) at which the progress of exonuclease III digestion is blocked by 82Q (−56) and by RNAP (−25). The red DNA segment is the consensus extended −10 element; σ70 region 2 is shown bound to the non-template strand. The RNAP outline is dashed to indicate that it does not depict a barrier to exonuclease digestion. We note that a barrier corresponding to the RNAP-dependent barrier at −25 also is seen in paused complexes formed on the wild-type 82 PR' template (where it occurs at position −4 relative to the 82 PR' transcription start site) (data not shown), and likely is caused by σ70 regions 2 and 3.
- Effect of removing σ70 region 4. Initiation complexes were formed with RNAP reconstituted with σ70 lacking region 4, σ70 1-529 (lanes 1-6 and 8-13). These complexes were then incubated with 20 nM 82Q (lanes 1-6) or no 82Q (lanes 8-13) and challenged with exonuclease III for the indicated times. Control assays were performed using template DNA incubated with 20 nM 82Q only (lanes 15-18). Lanes 7 and 14 contain A+G sequencing ladders.
