Figure 6.
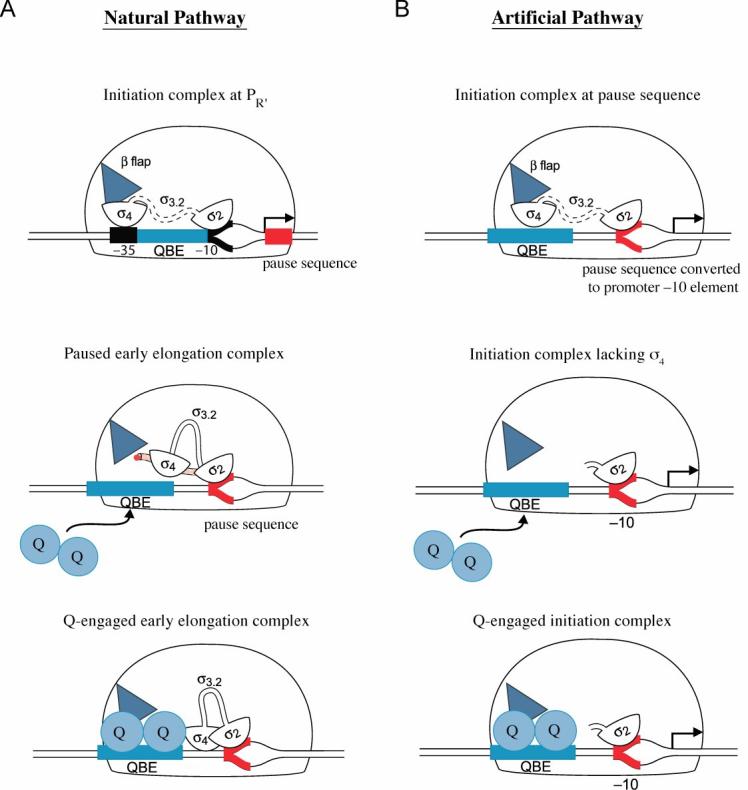
- Q engages a paused early elongation complex. Top panel depicts the PR' initiation complex in which σ region 3.2 (σ3.2) is located within the RNA exit channel and σ region 4 (σ4) is bound to the β flap (blue triangle). The pause-inducing sequence is shown in red. Middle panel depicts the paused early elongation complex in which the nascent RNA (shown as red beads emerging from the exit channel) has displaced σ region 3.2 (σ3.2) from the RNA exit channel and displaced σ region 4 (σ4) from the β flap. Bottom panel depicts Q-engaged early elongation complex.
- Q engages an initiation complex. Top panel depicts a wild-type initiation complex bound at a promoter created by converting the pause-inducing sequence to a consensus extended −10 element (shown in red). Middle panel depicts an initiation complex lacking σ region 4 bound at the converted pause-inducing sequence. Bottom panel depicts the Q-engaged initiation complex lacking σ region 4.
